In Vitro Time-Kill Studies of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia versus Escherichia coli Using Cation-Adjusted Mueller-Hinton Broth and ISO-Sensitest Broth
- PMID: 35007135
- PMCID: PMC8923228
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.02167-21
In Vitro Time-Kill Studies of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia versus Escherichia coli Using Cation-Adjusted Mueller-Hinton Broth and ISO-Sensitest Broth
Abstract
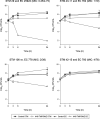
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMZ) is considered the treatment of choice for infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, but limited pharmacodynamic data are available to support current susceptibility breakpoints or guide optimal dosing. Time-kill studies using a TMP/SMZ concentration of 4/40 μg/mL were conducted to compare 4 S. maltophilia with 4 Escherichia coli isolates having the same MICs (0.25/4.75 to 4/76 μg/mL) in cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth (CAMHB) and ISO-Sensitest broth (ISO broth). With the exception of the resistant isolates (4/76 μg/mL), which resulted in regrowth approaching the growth of the control, TMP/SMZ displayed significantly greater killing for E. coli than for S. maltophilia at each MIC. Against E. coli, the mean changes at 24 h were -4.49, -1.73, -1.59, and +1.83 log10 CFU for isolates with MICs of 0.25/4.75, 1/19, 2/39, and 4/74 μg/mL, respectively. The area under the concentration-time curve for the free, unbound fraction of the drug (fAUC)/MIC ratio required for stasis and 1-log10 and 2-log10 CFU reductions were 40.7, 59.5, and 86.3, respectively. In contrast, TMP/SMZ displayed no stasis or CFU reductions against any S. maltophilia isolate regardless of the MIC, and no pharmacodynamic thresholds were quantifiable. Observations were consistent in both CAMHB and ISO broth. These data add increasing evidence that current TMP/SMZ susceptibility breakpoints against S. maltophilia should be reassessed.
Keywords: Gram negative; in vitro; pharmacodynamics; susceptibility breakpoint.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
We have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2021. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 31st ed, CLSI supplement M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

