Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism and Extensive Deep Venous Thrombosis for Early Thrombus Removal
- PMID: 35008066
- PMCID: PMC8752335
- DOI: 10.5758/vsi.210061
Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism and Extensive Deep Venous Thrombosis for Early Thrombus Removal
Abstract
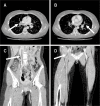
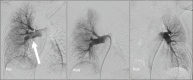
Traditional treatment with anticoagulation in nonfatal submassive pulmonary embolism can result in serious sequelae of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension or poor exercise tolerance, and functional impairment. To prevent long-term complications in previously healthy young patients, other treatment options to actively resolve existing thrombi should be considered. Despite recommendations for use in only severe clinical presentations, endovascular interventional techniques could serve as suitable treatment options for such patients. Here we report the case of a previously healthy 23-year-old female with submassive pulmonary embolism and extensive deep vein thrombosis in the inferior vena cava down to the right popliteal vein. The patient was initially treated with catheter-directed thrombolysis. However, she continued to show extensive venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Percutaneous thrombectomy and aspiration using an AngioJet successfully removed the main pulmonary artery embolism and venous thrombus. The patient's recovery was uneventful, and 3-month follow-up showed no signs of recurrence or discomfort.
Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis; Mechanical thrombolysis; Pulmonary embolism; Thrombolytic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Kline JA, Steuerwald MT, Marchick MR, Hernandez-Nino J, Rose GA. Prospective evaluation of right ventricular function and functional status 6 months after acute submassive pulmonary embolism: frequency of persistent or subsequent elevation in estimated pulmonary artery pressure. Chest. 2009;136:1202–1210. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-2988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

