Weight Change Alters the Small RNA Profile of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity
- PMID: 35008090
- PMCID: PMC9021654
- DOI: 10.1159/000521730
Weight Change Alters the Small RNA Profile of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity
Abstract
Introduction: Various kidney diseases reportedly show different urinary extracellular vesicle (EV) RNA profiles. Although obesity is one of the main causes of chronic kidney disease, the expression pattern of urinary EV RNA in obesity is uncertain. Our aim was to sequence the small RNA profiles of urinary EVs in obese patients before and after weight reduction and compare them to those of healthy volunteers (HVs).
Methods: We recruited age-sex-matched obese patients and HVs. The small RNA profiles of urinary EVs were analyzed using RNA sequencing. To evaluate the effect of weight reduction, small RNA profiles of urinary EVs 6 months after bariatric surgery were also analyzed.
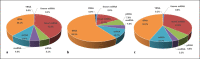
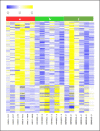
Results: The proportion of urinary EVs transfer RNA and microRNA of obese patients differed from that of HVs. Obese patients showed differential expression of 1,343 small RNAs in urinary EVs compared to HVs (fold change ≥2 and p value <0.05). Among those, 61 small RNAs were upregulated in obese patients and downregulated after weight reduction, whereas 167 small RNAs were downregulated in obese patients and upregulated after weight reduction. RNA sequencing revealed the correlation between the specific urinary EV small RNAs and clinical parameters including body weight, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, serum glucose, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and albuminuria.
Conclusion: Obese patients showed distinct urinary EV small RNA profiles compared to HVs. Weight reduction altered urinary EV small-RNA profiles in obese patients.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicle; Obesity; RNA; Small untranslated.
© 2022 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Obermayr RP, Temml C, Knechtelsdorfer M, Gutjahr G, Kletzmayr J, Heiss S, et al. Predictors of new-onset decline in kidney function in a general middle-european population. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008 Apr;23((4)):1265–1273. - PubMed
-
- Bolignano D, Zoccali C. Effects of weight loss on renal function in obese CKD patients: a systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Nov;28((Suppl 4)):iv82–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

