Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment and Ophthalmologist Consultations in Patients with Malignant Melanoma or Lung Cancer-A Nationwide Cohort Study
- PMID: 35008211
- PMCID: PMC8750081
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010049
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment and Ophthalmologist Consultations in Patients with Malignant Melanoma or Lung Cancer-A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
Purpose: To estimate the frequency of first-time ocular events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI).
Methods: Patients with cancer in 2011-2018 in Denmark were included and followed. The outcomes were first-time ophthalmologist consultation and ocular inflammation. One-year absolute risks of outcomes and hazard ratios were estimated.
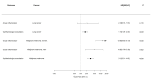
Results: 112,289 patients with cancer were included, and 2195 were treated with ICI. One year after the first ICI treatment, 6% of the patients with cancer, 5% and 8% of the lung cancer (LC) and malignant cutaneous melanoma (MM) patients, respectively, had a first-time ophthalmologist consultation. The risk of ocular inflammation was 1% (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.4-1.2). Among patients with MM, ICI was associated with ocular inflammation in women (HR 12.6 (95% CI 5.83-27.31) and men (4.87 (95% CI 1.79-13.29)). Comparing patients with and without ICI treatment, the risk of first-time ophthalmologist consultation was increased in patients with LC (HR 1.74 (95% CI 1.29-2.34) and MM (HR 3.21 (95% CI 2.31-4.44).
Conclusions: The one-year risks of first-time ophthalmologist consultation and ocular inflammation were 6% and 1%, respectively, in patients treated with ICI. In patients with LC and MM, the risk was increased in patients with ICI compared with patients without ICI.
Keywords: epidemiology; immune checkpoint inhibitors; lung cancer; malignant melanoma; ocular inflammation; one-year risk; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The risk of cardiac events in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a nationwide Danish study.Eur Heart J. 2021 Apr 21;42(16):1621-1631. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa884. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33291147
-
Association between immune checkpoint inhibitors and uveitis in patients with lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, or malignant melanoma.Can J Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 2:S0008-4182(25)00068-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2025.02.010. Online ahead of print. Can J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40118100
-
Cardiovascular adverse events are associated with usage of immune checkpoint inhibitors in real-world clinical data across the United States.ESMO Open. 2021 Oct;6(5):100252. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100252. Epub 2021 Aug 27. ESMO Open. 2021. PMID: 34461483 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Age on the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Combination Therapy for Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 23;10:1671. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01671. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33072551 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 24;12:701951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.701951. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34504488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ophthalmic immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1130238. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130238. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033964 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

