PCP4/PEP19 and HER2 Are Novel Prognostic Markers in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland
- PMID: 35008217
- PMCID: PMC8750196
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010054
PCP4/PEP19 and HER2 Are Novel Prognostic Markers in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland
Abstract
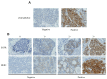
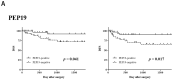
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is one of the most common malignant salivary gland carcinomas, but no effective treatment strategy has been established other than surgical resection. Purkinje cell protein (PCP) 4/peptide (PEP) 19 is a calmodulin-binding antiapoptotic peptide that is expressed and inhibits apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is an epidermal growth factor that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many carcinomas, particularly breast and gastric carcinomas. In the present study, we performed immunohistochemical analyses of samples from 73 patients who underwent surgical resection for MEC of the salivary gland using antibodies against PCP4/PEP19 and HER2. PCP4/PEP19 expression was related to better prognosis, while HER2 expression was associated with worse prognosis. Patients that were PCP4/PEP19-positive and HER2-negative showed similar outcomes to PCP4/PEP19 and HER2 alone. Therefore, PCP4/PEP19 and HER2 are predicted to play important roles in the pathogenesis and progression of MEC.
Keywords: Purkinje cell protein 4/peptide 19; human epidermal growth factor 2; mucoepidermoid carcinoma; prognosis; salivary gland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PCP4/PEP19 promotes migration, invasion and adhesion in human breast cancer MCF-7 and T47D cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):49065-49074. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7529. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384474 Free PMC article.
-
PCP4/PEP19 upregulates aromatase gene expression via CYP19A1 promoter I.1 in human breast cancer SK-BR-3 cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 3;9(51):29619-29633. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25651. eCollection 2018 Jul 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30038708 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-apoptotic effects of PCP4/PEP19 in human breast cancer cell lines: a novel oncotarget.Oncotarget. 2014 Aug 15;5(15):6076-86. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2161. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25153723 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary gland-like tumors of the breast express basal-type immunohistochemical markers.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2013 Jul;21(4):283-6. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e31826a277e. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2013. PMID: 22935826 Review.
-
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the breast shares cytogenetic abnormality with mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary gland: a case report with molecular analysis and review of the literature.Hum Pathol. 2009 Jun;40(6):887-92. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2008.11.004. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Hum Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19200580 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Targets in Salivary Gland Cancers: A Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of 118 Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Tumors.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 10;11(2):519. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020519. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831055 Free PMC article.
-
Aggressive Primary Thyroid Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma with Extensive Pulmonary Involvement.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 26;12(2):285. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020285. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397887 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis Based on EPOR Expression With Potential Value in Prognosis and Tumor Immunity in 33 Tumors.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 14;12:844794. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.844794. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35359375 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Aspects of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma and Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland.Head Neck Pathol. 2024 Apr 24;18(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s12105-024-01629-2. Head Neck Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38658430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland: Demographics and Comparative Analysis in U.S. Children and Adults with Future Perspective of Management.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;15(1):250. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010250. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rapidis A.D., Givalos N., Gakiopoulou H., Stavrianos S.D., Faratzis G., Lagogiannis G.A., Katsilieris I., Patsouris E. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. Review of the literature and clinicopathological analysis of 18 patients. Oral Oncol. 2007;43:130–136. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.03.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- El-Naggar A., Chan J., Grandis J., Takata T., Slootweg P. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumors. 4th ed. IARC; Lyon, France: 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

