Systematic Investigation of Biocompatible Cationic Polymeric Nucleic Acid Carriers for Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35008249
- PMCID: PMC8750096
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010085
Systematic Investigation of Biocompatible Cationic Polymeric Nucleic Acid Carriers for Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
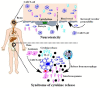
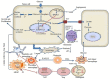
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third-largest cause of cancer death worldwide, while immunotherapy is rapidly being developed to fight HCC with great potential. Nucleic acid drugs are the most important modulators in HCC immunotherapy. To boost the efficacy of therapeutics and amplify the efficiency of genetic materials, biocompatible polymers are commonly used. However, under the strong need of a summary for current developments of biocompatible polymeric nucleic acid carriers for immunotherapy of HCC, there is rare review article specific to this topic to our best knowledge. In this article, we will discuss the current progress of immunotherapy for HCC, biocompatible cationic polymers (BCPs) as nucleic acid carriers used (or potential) to fight HCC, the roles of biocompatible polymeric carriers for nucleic acid delivery, and nucleic acid delivery by biocompatible polymers for immunotherapy. At the end, we will conclude the review and discuss future perspectives. This article discusses biocompatible polymeric nucleic acid carriers for immunotherapy of HCC from multidiscipline perspectives and provides a new insight in this domain. We believe this review will be interesting to polymer chemists, pharmacists, clinic doctors, and PhD students in related disciplines.
Keywords: biocompatible cationic polymers; gene intervention; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chan A.W., Zhong J., Berhane S., Toyoda H., Cucchetti A., Shi K., Tada T., Chong C.C., Xiang B.D., Li L.Q., et al. Development of pre and post-operative models to predict early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. J. Hepatol. 2018;69:1284–1293. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stanaway J.D., Flaxman A.D., Naghavi M., Fitzmaurice C., Vos T., Abubakar I., Abu-Raddad L.J., Assadi R., Bhala N., Cowie B., et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;388:1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30579-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xie Y. Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017;1018:11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

