Salvage Therapy for Relapsed Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35008346
- PMCID: PMC8750103
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010182
Salvage Therapy for Relapsed Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
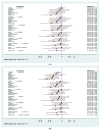
Patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) have very poor prognoses, and pemetrexed plus platinum is the standard first-line therapy. However, the second-line therapy for relapsed MPM remains controversial. A comprehensive search was performed to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating various second-line regimens in patients with relapsed MPM. Indirect comparisons of overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were performed using network meta-analysis. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) values were used to rank the included treatments according to each outcome. Nivolumab alone or nivolumab plus ipilimumab provided significantly longer OS than placebo (hazard ratio (HR): 0.72, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.55-0.94 for nivolumab alone; HR: 0.54, 95% CI: 0.31-0.92 for nivolumab plus ipilimumab). The best SUCRA ranking for OS was identified for nivolumab plus ipilimumab (SUCRA: 90.8%). Tremelimumab, vorinostat, nivolumab alone, chemotherapy (CTX), asparagine-glycine-arginine-human tumor necrosis factor plus CTX, and nivolumab plus ipilimumab all produced noticeable PFS benefits compared with placebo. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab had the best PFS ranking (SUCRA: 92.3%). Second-line treatment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab provided the OS and PFS outcomes for patients with relapsed MPM.
Keywords: NGR-hTNF; anetumab; chemotherapy; ipilimumab; malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM); network meta-analysis; nivolumab; pembrolizumab; tremelimumab; vorinostat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Feb;20(2):239-253. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30765-4. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30660609 Clinical Trial.
-
First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from CheckMate 743.Ann Oncol. 2022 May;33(5):488-499. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.01.074. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Ann Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35124183 Clinical Trial.
-
Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Combination with Chemotherapy as a First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;12(12):3629. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123629. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287455 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Drugs. 2021 Jun;81(9):971-984. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01506-0. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34106454 Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis of First-Line Treatments for Unresectable Pleural Mesothelioma: Indirect Comparisons from Reconstructed Individual Patient Data of Six Randomized Controlled Trials.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;17(3):503. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030503. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles: biogenesis mechanism and impacts on tumor immune microenvironment.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Sep 4;32(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01182-2. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 40908470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events in older patients with lung cancer: a prospective real-world analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(11):8993-9006. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04792-1. Epub 2023 May 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37160811 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and predictive biomarkers in malignant mesothelioma: Work still in progress.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1121557. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121557. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_0000370 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the miR-502-5p/SIRT1 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2024 Apr;62(2):1231-1247. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10468-9. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37561331
-
LncRNA SNHG1 Accelerates Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Hepatoblastoma Through Mediating miR-6838-5p/PIM3/RhoA Axis.Biochem Genet. 2024 Feb;62(1):59-76. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10404-x. Epub 2023 May 29. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37248373
References
-
- Scherpereel A., Astoul P., Baas P., Berghmans T., Clayson H., de Vuyst P., Dienemann H., Galateau-Salle F., Hennequin C., Hillerdal G., et al. Guidelines of the European Respiratory Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2010;35:479–495. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00063109. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

