Phototheranostics of Cervical Neoplasms with Chlorin e6 Photosensitizer
- PMID: 35008375
- PMCID: PMC8750251
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010211
Phototheranostics of Cervical Neoplasms with Chlorin e6 Photosensitizer
Abstract
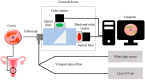
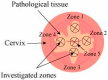
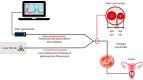
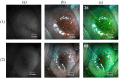
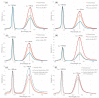
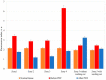
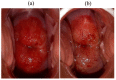
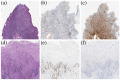
(1) Purpose: Improving the treatment effectiveness of intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix associated with human papillomavirus infection, based on the application of the method of photodynamic therapy with simultaneous laser excitation of fluorescence to clarify the boundaries of cervical neoplasms. (2) Methods: Examination and treatment of 52 patients aged 22 to 53 years with morphologically and cytologically confirmed mild to severe intraepithelial cervix neoplasia, preinvasive, micro-invasive, and squamous cell cervix carcinoma. All patients were carriers of human papillomavirus infection. The patients underwent photodynamic therapy with simultaneous laser excitation of fluorescence. The combined use of video and spectral fluorescence diagnostics for cervical neoplasms made it possible to control the photodynamic therapy process at all stages of the procedure. Evaluation of the photodynamic therapy of intraepithelial cervical neoplasms was carried out with colposcopic examination, cytological conclusion, and morphological verification of the biopsy material after the photodynamic therapy course. The success of human papillomavirus therapy was assessed based on the results of the polymerase chain reaction. (3) Results. The possibility of simultaneous spectral fluorescence diagnostics and photodynamic therapy using a laser source with a wavelength of 660 nm has been established, making it possible to assess the fluorescence index in real-time and control the photobleaching of photosensitizers in the irradiated area. The treatment of all 52 patients was successful after the first photodynamic therapy procedure. According to the PCR test of the discharge from the cervical canal, the previously identified HPV types were not observed in 48 patients. Previously identified HPV types were absent after repeated PDT in four patients (CIN III (n = 2), CIS (n = 2)). In 80.8% of patients, regression of the lesion was noted. (4) Conclusions. The high efficiency of photodynamic therapy with intravenous photosensitizer administration of chlorin e6 has been demonstrated both in relation to eradication therapy of human papillomavirus and in relation to the treatment of intraepithelial lesions of the cervix.
Keywords: cervical cancer; cervical dysplasia; human papillomavirus; organ-preserving treatment; photodiagnostics; photodynamic therapy; phototheranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the Results of Severe Intraepithelial Squamous Cell Lesions and Preinvasive Cervical Cancer Phototheranostics in Women of Reproductive Age.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 9;10(10):2521. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102521. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289783 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of treatment efficacy in severe intraepithelial squamous cell lesions and preinvasive cervical cancer by conization and chlorin e6-mediated fluorescence-assisted systemic photodynamic therapy.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024 Apr;46:104060. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2024.104060. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38521149 Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor fluorescence and oxygenation monitoring during photodynamic therapy with chlorin e6 photosensitizer.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024 Feb;45:103969. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2024.103969. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38211779
-
[Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for early cervical cancer].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1996 Jan;23(1):47-56. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1996. PMID: 8546469 Review. Japanese.
-
Photodynamic therapy of cervical cancer: a scoping review on the efficacy of various molecules.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024 Mar 4;15:20406223241233206. doi: 10.1177/20406223241233206. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024. PMID: 38440782 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanotherapeutic Intervention in Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):45882-45909. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05852. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined use of 5-ALA-induced protoporphyrin IX and chlorin e6 for fluorescence diagnostics and photodynamic therapy of skin tumors.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Oct 31;39(1):266. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04219-4. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39477891
-
Analysis of the Results of Severe Intraepithelial Squamous Cell Lesions and Preinvasive Cervical Cancer Phototheranostics in Women of Reproductive Age.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 9;10(10):2521. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102521. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289783 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Photodynamic Treatment of Precancerous and Cancerous Gynecological Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 22;17(15):2421. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152421. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Cancer Treatment: Innovative Materials in PDT and Diagnostic Integration.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 May 31;20:7037-7060. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S514937. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40470109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization; [(accessed on 24 October 2021)]. Cancer Today, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/
-
- World Health Organization; [(accessed on 12 November 2021)]. Cancer Tomorrow, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en.
-
- D’arc M., Moreira F.R.R., Dias C.A., Souza A.R., Seuánez H.N., Soares M.A., Tavares M.C.H., Santos A.F.A. The characterization of two novel neotropical primate papillomaviruses supports the ancient within-species diversity model. Virus Evol. 2020;6:veaa036. doi: 10.1093/ve/veaa036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

