Synergistic Action of Immunotherapy and Nanotherapy against Cancer Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and the Use of Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 35008377
- PMCID: PMC8750412
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010213
Synergistic Action of Immunotherapy and Nanotherapy against Cancer Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and the Use of Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
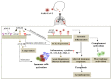
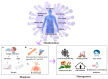
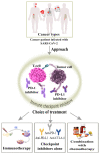
Since 2019, the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has caused a huge chaos throughout the world and the major threat has been possessed by the immune-compromised individuals involving the cancer patients; their weakened immune response makes them vulnerable and susceptible to the virus. The oncologists as well as their patients are facing many problems for their treatment sessions as they need to postpone their surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy. The approach that could be adopted especially for the cancer patients is the amalgamation of immunotherapy and nanotherapy which can reduce the burden on the healthcare at this peak time of the infection. There is also a need to predict or analyze the data of cancer patients who are at a severe risk of being exposed to an infection in order to reduce the mortality rate. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) could be incorporated where the real time data will be available to the physicians according to the different patient's clinical characteristics and their past treatments. With this data, it will become easier for them to modify or replace the treatment to increase the efficacy against the infection. The combination of an immunotherapy and nanotherapy will be targeted to treat the cancer patients diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 and the AI will act as icing on the cake to monitor, predict and analyze the data of the patients to improve the treatment regime for the most vulnerable patients.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cancer; immunotherapy; nanotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships which could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Severity of COVID-19 in patients with lung cancer: evidence and challenges.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Mar;9(3):e002266. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002266. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33737345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyzing the impact of machine learning and artificial intelligence and its effect on management of lung cancer detection in covid-19 pandemic.Mater Today Proc. 2022;56:2213-2216. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.549. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Mater Today Proc. 2022. PMID: 34877264 Free PMC article.
-
The Rapid Development and Early Success of Covid 19 Vaccines Have Raised Hopes for Accelerating the Cancer Treatment Mechanism.Arch Razi Inst. 2021 Mar;76(1):1-6. doi: 10.22092/ari.2021.353761.1612. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Arch Razi Inst. 2021. PMID: 33818952 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence approach fighting COVID-19 with repurposing drugs.Biomed J. 2020 Aug;43(4):355-362. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 15. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32426387 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Jul-Aug;14(4):337-339. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.012. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32305024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chan J.F.W., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K.W., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C.Y., Poon R.W.S., et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- NCKUH-11002002/National Cheng Kung University Hospital
- MOST 109-2314-B-006-078, 110-2314-B-006-108, 109-2314-B-006-084-MY3, and MOST 110-2321-B-006-005)/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- NCKUEDA11005/E-DA hospital
- MOHW 110-TDU-B-212-124006/Department of Urology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

