Contribution of LAT1-4F2hc in Urological Cancers via Toll-like Receptor and Other Vital Pathways
- PMID: 35008399
- PMCID: PMC8750950
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14010229
Contribution of LAT1-4F2hc in Urological Cancers via Toll-like Receptor and Other Vital Pathways
Abstract
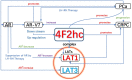
Tumor cells are known for their ability to proliferate. Nutrients are essential for rapidly growing tumor cells. In particular, essential amino acids are essential for tumor cell growth. Tumor cell growth nutrition requires the regulation of membrane transport proteins. Nutritional processes require amino acid uptake across the cell membrane. Leucine, one of the essential amino acids, has recently been found to be closely associated with cancer, which activate mTOR signaling pathway. The transport of leucine into cells requires an L-type amino acid transporter protein 1, LAT1 (SLC7A5), which requires the 4F2 cell surface antigen heavy chain (4F2hc, SLC3A2) to form a heterodimeric amino acid transporter protein complex. Recent evidence identified 4F2hc as a specific downstream target of the androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7). We stressed the importance of the LAT1-4F2hc complex as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in urological cancers in this review, which covered the recent achievements in research on the involvement of the LAT1-4F2hc complex in urinary system tumors. In addition, JPH203, which is a selective LAT1 inhibitor, has shown excellent inhibitory effects on the proliferation in a variety of tumor cells. The current phase I clinical trials of JPH203 in patients with biliary tract cancer have also achieved good results, which is the future research direction for LAT1 targeted therapy drugs.
Keywords: 4F2 cell-surface antigen heavy chain (4F2hc, SLC3A2); L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1, SLC7A); diagnosis; targeted therapy; urinary system tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
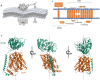
Structure of the human LAT1-4F2hc heteromeric amino acid transporter complex.Nature. 2019 Apr;568(7750):127-130. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1011-z. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30867591
-
The human LAT1-4F2hc (SLC7A5-SLC3A2) transporter complex: Physiological and pathophysiological implications.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Nov;133(5):459-472. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13821. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36460306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast Cell-Based Transport Assay for the Functional Characterization of Human 4F2hc-LAT1 and -LAT2, and LAT1 and LAT2 Substrates and Inhibitors.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 28;8:676854. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.676854. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34124158 Free PMC article.
-
Pichia pastoris and the Recombinant Human Heterodimeric Amino Acid Transporter 4F2hc-LAT1: From Clone Selection to Pure Protein.Methods Protoc. 2021 Jul 24;4(3):51. doi: 10.3390/mps4030051. Methods Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34449687 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid transporter LAT1 (SLC7A5) as a molecular target for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;230:107964. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107964. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34390745 Review.
Cited by
-
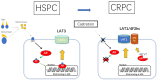
Contribution of the L-Type Amino Acid Transporter Family in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6178. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076178. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
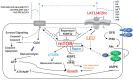
The LAT1 inhibitor JPH203 suppresses the growth of castration-resistant prostate cancer through a CD24-mediated mechanism.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jul;115(7):2461-2472. doi: 10.1111/cas.16191. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38655663 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes containing miR-152-3p targeting FGFR3 mediate SLC7A7-induced angiogenesis in bladder cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Mar 12;9(1):71. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00859-z. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40075158 Free PMC article.
-
m6A modification mediates SLC3A2/SLC7A5 translation in 3-methylcholanthrene-induced uroepithelial transformation.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jan 25;40(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09846-9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38267663 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Carrying miR-887-3p Promote Breast Cancer Cell Drug Resistance by Targeting BTBD7 and Activating the Notch1/Hes1 Signaling Pathway.Dis Markers. 2022 May 23;2022:5762686. doi: 10.1155/2022/5762686. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35655918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qi W., Guan Q., Sun T., Cao Y., Zhang L., Guo Y. Improving detection sensitivity of amino acids in thyroid tissues by using phthalic acid as a mobile phase additive in hydrophilic interaction chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2015;870:75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirikae M., Diksic M., Yamamoto Y.L. Quantitative measurements of regional glucose utilization and rate of valine incorporation into proteins by double-tracer autoradiography in the rat brain tumor model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1989;9:87–95. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.12. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

