Environmental Factors That Affect Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin Levels
- PMID: 35008468
- PMCID: PMC8744774
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010044
Environmental Factors That Affect Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin Levels
Abstract
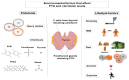
Calciotropic hormones, parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin are involved in the regulation of bone mineral metabolism and maintenance of calcium and phosphate homeostasis in the body. Therefore, an understanding of environmental and genetic factors influencing PTH and calcitonin levels is crucial. Genetic factors are estimated to account for 60% of variations in PTH levels, while the genetic background of interindividual calcitonin variations has not yet been studied. In this review, we analyzed the literature discussing the influence of environmental factors (lifestyle factors and pollutants) on PTH and calcitonin levels. Among lifestyle factors, smoking, body mass index (BMI), diet, alcohol, and exercise were analyzed; among pollutants, heavy metals and chemicals were analyzed. Lifestyle factors that showed the clearest association with PTH levels were smoking, BMI, exercise, and micronutrients taken from the diet (vitamin D and calcium). Smoking, vitamin D, and calcium intake led to a decrease in PTH levels, while higher BMI and exercise led to an increase in PTH levels. In terms of pollutants, exposure to cadmium led to a decrease in PTH levels, while exposure to lead increased PTH levels. Several studies have investigated the effect of chemicals on PTH levels in humans. Compared to PTH studies, a smaller number of studies analyzed the influence of environmental factors on calcitonin levels, which gives great variability in results. Only a few studies have analyzed the influence of pollutants on calcitonin levels in humans. The lifestyle factor with the clearest relationship with calcitonin was smoking (smokers had increased calcitonin levels). Given the importance of PTH and calcitonin in maintaining calcium and phosphate homeostasis and bone mineral metabolism, additional studies on the influence of environmental factors that could affect PTH and calcitonin levels are crucial.
Keywords: PTH; calcitonin; calcium; environmental factors; lifestyle factors; phosphate; pollutants; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tebben P.J., Kumar R. Seldin and Geibisch’s The Kidney. Volume 2. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. The hormonal regulation of calcium metabolism; pp. 2249–2272.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

