Galectins in Early Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Associated Pathologies
- PMID: 35008499
- PMCID: PMC8744741
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010069
Galectins in Early Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Associated Pathologies
Abstract
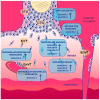
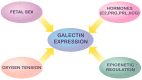
Galectins are a family of conserved soluble proteins defined by an affinity for β-galactoside structures present on various glycoconjugates. Over the past few decades, galectins have been recognized as important factors for successful implantation and maintenance of pregnancy. An increasing number of studies have demonstrated their involvement in trophoblast cell function and placental development. In addition, several lines of evidence suggest their important roles in feto-maternal immune tolerance regulation and angiogenesis. Changed or dysregulated galectin expression is also described in pregnancy-related disorders. Although the data regarding galectins' clinical relevance are still at an early stage, evidence suggests that some galectin family members are promising candidates for better understanding pregnancy-related pathologies, as well as predicting biomarkers. In this review, we aim to summarize current knowledge of galectins in early pregnancy as well as in pregnancy-related pathologies.
Keywords: galectins; pregnancy; pregnancy-related pathologies; trophoblast function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

