Extension of the Human Fibrinogen Database with Detailed Clinical Information-The αC-Connector Segment
- PMID: 35008554
- PMCID: PMC8745514
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010132
Extension of the Human Fibrinogen Database with Detailed Clinical Information-The αC-Connector Segment
Abstract
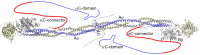
Fibrinogen, an abundant plasma glycoprotein, is involved in the final stage of blood coagulation. Decreased fibrinogen levels, which may be caused by mutations, are manifested mainly in bleeding and thrombotic disorders. Clinically relevant mutations of fibrinogen are listed in the Human Fibrinogen Database. For the αC-connector (amino acids Aα240-410, nascent chain numbering), we have extended this database, with detailed descriptions of the clinical manifestations among members of reported families. This includes the specification of bleeding and thrombotic events and results of coagulation assays. Where available, the impact of a mutation on clotting and fibrinolysis is reported. The collected data show that the Human Fibrinogen Database reports considerably fewer missense and synonymous mutations than the general COSMIC and dbSNP databases. Homozygous nonsense or frameshift mutations in the αC-connector are responsible for most clinically relevant symptoms, while heterozygous mutations are often asymptomatic. Symptomatic subjects suffer from bleeding and, less frequently, from thrombotic events. Miscarriages within the first trimester and prolonged wound healing were reported in a few subjects. All mutations inducing thrombotic phenotypes are located at the identical positions within the consensus sequence of the tandem repeats.
Keywords: Human Fibrinogen Database; afibrinogenemia; dysfibrinogenemia; fibrinogen; hypodysfibrinogenemia; hypofibrinogenemia; mutations; αC-connector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chargaff E., Bendich A. On the coagulation of fibrinogen. J. Biol. Chem. 1943;149:93–110. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)72219-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

