Protective Effect of Low-Dose Alcohol Consumption against Post-Ischemic Neuronal Apoptosis: Role of L-PGDS
- PMID: 35008575
- PMCID: PMC8745720
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010133
Protective Effect of Low-Dose Alcohol Consumption against Post-Ischemic Neuronal Apoptosis: Role of L-PGDS
Abstract
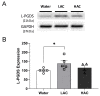
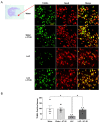
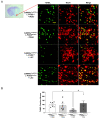
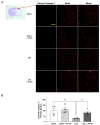
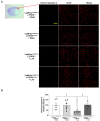
Ischemic stroke is one of the leading causes of permanent disability and death in adults worldwide. Apoptosis is a major element contributing to post-ischemic neuronal death. We previously found that low-dose alcohol consumption (LAC) protects against neuronal apoptosis in the peri-infarct cortex following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D2 synthase (L-PGDS), which is mainly localized in the central nervous system (CNS), was previously shown to inhibit neuronal apoptosis. Therefore, we determined whether L-PGDS is involved in the protective effect of LAC against post-ischemic neuronal apoptosis. Wild-type (WT), CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDS+/+, and CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDSflox/flox mice on a C57BL/6J background were gavage fed with ethanol or volume-matched water once a day for 8 weeks. Tamoxifen (2 mg/day) was given intraperitoneally to CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDS+/+ and CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDSflox/flox mice for 5 days during the fourth week. AT-56 (30 mg/kg/day), a selective inhibitor of L-PGDS, was given orally to AT-56-treated WT mice from the fifth week for four weeks. Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, TUNEL-positive neurons, and cleaved caspase-3-positive neurons were measured at 24 h of reperfusion after a 90 min unilateral middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). We found that 0.7 g/kg/day but not 2.8 g/kg/day ethanol significantly upregulated L-PGDS in the cerebral cortex. In addition, 0.7 g/kg/day ethanol diminished cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and TUNEL-positive and cleaved caspase-3-positive neurons in the peri-infarct cortex in WT and CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDS+/+ mice. Furthermore, the neuroprotective effect of 0.7 g/kg/day ethanol was alleviated in AT-56-treated WT and CaMKIIαCreERT2/+/L-PGDSflox/flox mice. Our findings suggest that LAC may protect against cerebral I/R injury by suppressing post-ischemic neuronal apoptosis via an upregulated L-PGDS.
Keywords: L-PGDS; apoptosis; brain; ethanol; ischemic stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Blaha M.J., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Das S.R., Deo R., de Ferranti S.D., Floyd J., Fornage M., Gillespie C., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–e603. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

