A Review of the Current Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: Have We Hit the Bullseye Yet?
- PMID: 35008685
- PMCID: PMC8745775
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010259
A Review of the Current Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: Have We Hit the Bullseye Yet?
Abstract
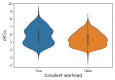
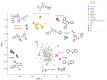
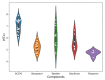
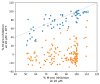
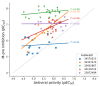
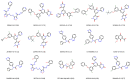
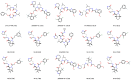
In this review, we collected 1765 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) M-pro inhibitors from the bibliography and other sources, such as the COVID Moonshot project and the ChEMBL database. This set of inhibitors includes only those compounds whose inhibitory capacity, mainly expressed as the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value, against M-pro from SARS-CoV-2 has been determined. Several covalent warheads are used to treat covalent and non-covalent inhibitors separately. Chemical space, the variation of the IC50 inhibitory activity when measured by different methods or laboratories, and the influence of 1,4-dithiothreitol (DTT) are discussed. When available, we have collected the values of inhibition of viral replication measured with a cellular antiviral assay and expressed as half maximal effective concentration (EC50) values, and their possible relationship to inhibitory potency against M-pro is analyzed. Finally, the most potent covalent and non-covalent inhibitors that simultaneously inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 M-pro and the virus replication in vitro are discussed.
Keywords: 3CL-pro inhibitors; COVID-19; M-pro inhibitors; computational chemistry; protease inhibitors; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gimeno A., Mestres-Truyol J., Ojeda-Montes M.J., Macip G., Saldivar-Espinoza B., Cereto-Massagué A., Pujadas G., Garcia-Vallvé S. Prediction of Novel Inhibitors of the Main Protease (M-pro) of SARS-CoV-2 through Consensus Docking and Drug Reposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:3793. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kneller D.W., Phillips G., O’Neill H.M., Jedrzejczak R., Stols L., Langan P., Joachimiak A., Coates L., Kovalevsky A. Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Mpro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:3202. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16954-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

