Mapping and Characterization of HCMV-Specific Unconventional HLA-E-Restricted CD8 T Cell Populations and Associated NK and T Cell Responses Using HLA/Peptide Tetramers and Spectral Flow Cytometry
- PMID: 35008688
- PMCID: PMC8745070
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010263
Mapping and Characterization of HCMV-Specific Unconventional HLA-E-Restricted CD8 T Cell Populations and Associated NK and T Cell Responses Using HLA/Peptide Tetramers and Spectral Flow Cytometry
Abstract
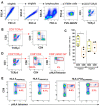
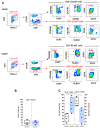
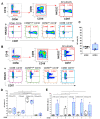
HCMV drives complex and multiple cellular immune responses, which causes a persistent immune imprint in hosts. This study aimed to achieve both a quantitative determination of the frequency for various anti-HCMV immune cell subsets, including CD8 T, γδT, NK cells, and a qualitative analysis of their phenotype. To map the various anti-HCMV cellular responses, we used a combination of three HLApeptide tetramer complexes (HLA-EVMAPRTLIL, HLA-EVMAPRSLLL, and HLA-A2NLVPMVATV) and antibodies for 18 surface markers (CD3, CD4, CD8, CD16, CD19, CD45RA, CD56, CD57, CD158, NKG2A, NKG2C, CCR7, TCRγδ, TCRγδ2, CX3CR1, KLRG1, 2B4, and PD-1) in a 20-color spectral flow cytometry analysis. This immunostaining protocol was applied to PBMCs isolated from HCMV- and HCMV+ individuals. Our workflow allows the efficient determination of events featuring HCMV infection such as CD4/CD8 ratio, CD8 inflation and differentiation, HCMV peptide-specific HLA-EUL40 and HLA-A2pp65CD8 T cells, and expansion of γδT and NK subsets including δ2-γT and memory-like NKG2C+CD57+ NK cells. Each subset can be further characterized by the expression of 2B4, PD-1, KLRG1, CD45RA, CCR7, CD158, and NKG2A to achieve a fine-tuned mapping of HCMV immune responses. This assay should be useful for the analysis and monitoring of T-and NK cell responses to HCMV infection or vaccines.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; HCMV; HLA-E; NK; pHLA tetramers; spectral flow cytometry; γδT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinctive phenotype for HLA-E- versus HLA-A2-restricted memory CD8 αβT cells in the course of HCMV infection discloses features shared with NKG2C+CD57+NK and δ2-γδT cell subsets.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1063690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1063690. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532017 Free PMC article.
-
HCMV triggers frequent and persistent UL40-specific unconventional HLA-E-restricted CD8 T-cell responses with potential autologous and allogeneic peptide recognition.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Apr 30;14(4):e1007041. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007041. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29709038 Free PMC article.
-
NKG2C(+)CD57(+) Natural Killer Cell Expansion Parallels Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Evolution towards Senescence.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:7470124. doi: 10.1155/2016/7470124. Epub 2016 May 29. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27314055 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of HCMV-specific immune responses: Parallels between CD8(+) T cells, CD4(+) T cells, and NK cells.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Sep;45(9):2433-45. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545495. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26228786 Review.
-
Human leukocyte antigen E in human cytomegalovirus infection: friend or foe?Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2012 Jul;44(7):551-4. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gms032. Epub 2012 May 9. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2012. PMID: 22576308 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinctive phenotype for HLA-E- versus HLA-A2-restricted memory CD8 αβT cells in the course of HCMV infection discloses features shared with NKG2C+CD57+NK and δ2-γδT cell subsets.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1063690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1063690. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532017 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of NKG2-A/-C, Kir and CD57 on NK Cells Stimulated with pp65 and IE-1 Antigens in Patients Awaiting Lung Transplant.Life (Basel). 2022 Jul 19;12(7):1081. doi: 10.3390/life12071081. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35888169 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-E-restricted Hantaan virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses enhance the control of infection in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.Biosaf Health. 2023 Jun 16;5(5):289-299. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.06.002. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biosaf Health. 2023. PMID: 40078905 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in HCMV immune cell frequency and phenotype are associated with chronic lung allograft dysfunction.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1143875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1143875. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37187736 Free PMC article.
-
Memory inflation: Beyond the acute phase of viral infection.Cell Prolif. 2024 Dec;57(12):e13705. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13705. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38992867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sylwester A.W., Mitchell B.L., Edgar J.B., Taormina C., Pelte C., Ruchti F., Sleath P.R., Grabstein K.H., Hosken N.A., Kern F., et al. Broadly targeted human cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells dominate the memory compartments of exposed subjects. J. Exp. Med. 2005;202:673–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050882. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaminski H., Garrigue I., Couzi L., Taton B., Bachelet T., Moreau J.F., Dechanet-Merville J., Thiebaut R., Merville P. Surveillance of gammadelta T Cells Predicts Cytomegalovirus Infection Resolution in Kidney Transplants. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016;27:637–645. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014100985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

