Comparative Study of Two-Dimensional (2D) vs. Three-Dimensional (3D) Organotypic Kertatinocyte-Fibroblast Skin Models for Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection
- PMID: 35008727
- PMCID: PMC8745520
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010299
Comparative Study of Two-Dimensional (2D) vs. Three-Dimensional (3D) Organotypic Kertatinocyte-Fibroblast Skin Models for Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection
Abstract
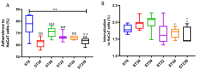
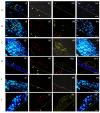
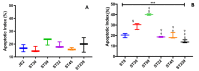
The invasion of skin tissue by Staphylococcus aureus is mediated by mechanisms that involve sequential breaching of the different stratified layers of the epidermis. Induction of cell death in keratinocytes is a measure of virulence and plays a crucial role in the infection progression. We established a 3D-organotypic keratinocyte-fibroblast co-culture model to evaluate whether a 3D-skin model is more effective in elucidating the differences in the induction of cell death by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) than in comparison to 2D-HaCaT monolayers. We investigated the difference in adhesion, internalization, and the apoptotic index in HaCaT monolayers and our 3D-skin model using six strains of MRSA representing different clonal types, namely, ST8, ST30, ST59, ST22, ST45 and ST239. All the six strains exhibited internalization in HaCaT cells. Due to cell detachment, the invasion study was limited up to two and a half hours. TUNEL assay showed no significant difference in the cell death induced by the six MRSA strains in the HaCaT cells. Our 3D-skin model provided a better insight into the interactions between the MRSA strains and the human skin during the infection establishment as we could study the infection of MRSA in our skin model up to 48 h. Immunohistochemical staining together with TUNEL assay in the 3D-skin model showed co-localization of the bacteria with the apoptotic cells demonstrating the induction of apoptosis by the bacteria and revealed the variation in bacterial transmigration among the MRSA strains. The strain representing ST59 showed maximum internalization in HaCaT cells and the maximum cell death as measured by Apoptotic index in the 3D-skin model. Our results show that 3D-skin model might be more likely to imitate the physiological response of skin to MRSA infection than 2D-HaCaT monolayer keratinocyte cultures and will enhance our understanding of the difference in pathogenesis among different MRSA strains.
Keywords: 3D skin model; HaCaT; MRSA; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wong J.W.H., Ip M., Tang A., Wei V.W.I., Wong S.Y.S., Riley S., Read J.M., Kwok K.O. Prevalence and risk factors of community-associated methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus carriage in asia-pacific region from 2000 to 2016: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018;10:1489–1501. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S160595. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

