A Review on the Role of miR-149-5p in the Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 35008841
- PMCID: PMC8745060
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010415
A Review on the Role of miR-149-5p in the Carcinogenesis
Abstract
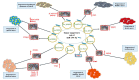
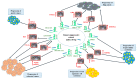
miR-149 is an miRNA with essential roles in carcinogenesis. This miRNA is encoded by the MIR149 gene on 2q37.3. The miR-149 hairpin produces miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p, which are the "guide" and the sister "passenger" strands, respectively. Deep sequencing experiments have shown higher prevalence of miR-149-5p compared with miR-149-3p. Notably, both oncogenic and tumor suppressive roles have been reported for miR-149-5p. In this review, we summarize the impact of miR-149-5p in the tumorigenesis and elaborate mechanisms of its involvement in this process in a variety of neoplastic conditions based on three lines of evidence, i.e., in vitro, in vivo and clinical settings.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; expression; miR-149-5p; ncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Khan R., Raza S.H.A., Junjvlieke Z., Wang X., Wang H., Cheng G., Mei C., Elnour I.E., Zan L. Bta-miR-149-5p inhibits proliferation and differentiation of bovine adipocytes through targeting CRTCs at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020;235:5796–5810. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29513. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

