New Proteins Contributing to Immune Cell Infiltration and Pannus Formation of Synovial Membrane from Arthritis Diseases
- PMID: 35008858
- PMCID: PMC8745719
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010434
New Proteins Contributing to Immune Cell Infiltration and Pannus Formation of Synovial Membrane from Arthritis Diseases
Abstract
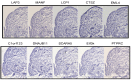
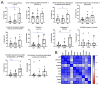
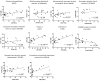
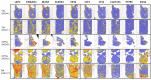
An inflamed synovial membrane plays a major role in joint destruction and is characterized by immune cells infiltration and fibroblast proliferation. This proteomic study considers the inflammatory process at the molecular level by analyzing synovial biopsies presenting a histological inflammatory continuum throughout different arthritis joint diseases. Knee synovial biopsies were obtained from osteoarthritis (OA; n = 9), chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy (CPPA; n = 7) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA; n = 8) patients. The histological inflammatory score was determined using a semi-quantitative scale based on synovial hyperplasia, lymphocytes, plasmocytes, neutrophils and macrophages infiltration. Proteomic analysis was performed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Differentially expressed proteins were confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Out of the 1871 proteins identified and quantified by LC-MS/MS, 10 proteins (LAP3, MANF, LCP1, CTSZ, PTPRC, DNAJB11, EML4, SCARA5, EIF3K, C1orf123) were differentially expressed in the synovial membrane of at least one of the three disease groups (RA, OA and CPPA). Significant increased expression of the seven first proteins was detected in RA and correlated to the histological inflammatory score. Proteomics is therefore a powerful tool that provides a molecular pattern to the classical histology usually applied for synovitis characterization. Except for LCP1, CTSZ and PTPRC, all proteins have never been described in human synovitis.
Keywords: CTSZ; DNAJB11; EML4; LAP3; LCP1; MANF; PTPRC; inflammation; proteomics; synovial membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteins involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress are modulated in synovitis of osteoarthritis, chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis, and correlate with the histological inflammatory score.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 4;10(1):14159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70803-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32887899 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial immunopathology in haemochromatosis arthropathy.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jun;69(6):1214-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.120204. Epub 2009 Nov 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 19933745
-
Chronically inflamed synovium from spondyloarthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis investigated by protein expression profiling followed by tandem mass spectrometry.Proteomics. 2005 May;5(8):2247-57. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200401109. Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 15846842
-
Morphological and molecular pathology of the B cell response in synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis.Virchows Arch. 2002 Nov;441(5):415-27. doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0702-1. Epub 2002 Nov 5. Virchows Arch. 2002. PMID: 12447670 Review.
-
Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(3):189-202. doi: 10.1186/ar86. Epub 2000 Apr 12. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11094428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and role of differentially expressed genes/proteins between pulmonary tuberculosis patients and controls across lung tissues and blood samples.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jul;12(7):e1350. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1350. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39023413 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds and Plant Extracts in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Comprehensive Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;13(7):775. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070775. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Analysis of the Immune Infiltration Pattern and Candidate Diagnostic Biomarkers in Lumbar Disc Herniation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Apr 21;15:846554. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.846554. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35531067 Free PMC article.
-
P4HA3 promotes colon cancer cell escape from macrophage phagocytosis by increasing phagocytosis immune checkpoint CD47 expression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Dec;479(12):3355-3374. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04927-z. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38347264
-
Analysis of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Immune Function During the Development of Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 16;13:901697. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901697. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35784282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang F., Wei K., Slowikowski K., Fonseka C.Y., Rao D.A., Kelly S., Goodman S.M., Tabechian D., Hughes L.B., Salomon-Escoto K., et al. Defining Inflammatory Cell States in Rheumatoid Arthritis Joint Synovial Tissues by Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomics and Mass Cytometry. Nat. Immunol. 2019;20:928–942. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0378-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

