Novel Risk Associations between microRNA Polymorphisms and Gastric Cancer in a Chilean Population
- PMID: 35008894
- PMCID: PMC8745138
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010467
Novel Risk Associations between microRNA Polymorphisms and Gastric Cancer in a Chilean Population
Abstract
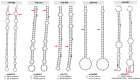
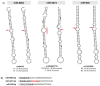
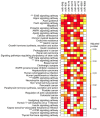
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth leading cause of cancer deaths in the world, with variations across geographical regions and ethnicities. Emerging evidence indicates that miRNA expression is dysregulated in GC and its polymorphisms may contribute to these variations, which has yet to be explored in Latin American populations. In a case-control study of 310 GC patients and 311 healthy donors from Chile, we assessed the association of 279 polymorphisms in 242 miRNA genes. Two novel polymorphisms were found to be associated with GC: rs4822739:C>G (miR-548j) and rs701213:T>C (miR-4427). Additionally, rs1553867776:T>TCCCCA (miR-4274) and rs12416605:C>T (miR-938) were associated with intestinal-type GC, and rs4822739:C>G (miR-548j) and rs1439619:T>G (miR-3175) with TNM I-II stage. The polymorphisms rs6149511:T> TGAAGGGCTCCA (miR-6891), rs404337:G>A (miR-8084), and rs1439619:T>G (miR-3175) were identified among H.pylori-infected GC patients and rs7500280:T>C (miR-4719) and rs1439619:T>G (miR-3175) were found among H. pylori cagPAI+ infected GC cases. Prediction analysis suggests that seven polymorphisms could alter the secondary structure of the miRNA, and the other one is located in the seed region of miR-938. Targets of miRNAs are enriched in GC pathways, suggesting a possible biological effect. In this study, we identified seven novel associations and replicated one previously described in Caucasian population. These findings contribute to the understanding of miRNA genetic polymorphisms in the GC pathogenesis.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; cag pathogenicity island; gastric cancer; miRNA; polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic association of gastric cancer with miRNA clusters including the cancer-related genes MIR29, MIR25, MIR93 and MIR106: results from the EPIC-EURGAST study.Int J Cancer. 2014 Nov 1;135(9):2065-76. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28850. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24643999
-
Associations of the -238(G/A) and -308(G/A) TNF-α Promoter Polymorphisms and TNF-α Serum Levels with the Susceptibility to Gastric Precancerous Lesions and Gastric Cancer Related to Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Moroccan Population.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Jun 1;21(6):1623-1629. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1623. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32592356 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Polymorphisms in three pri-miRNAs that Target Pepsinogen C with the Risk and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 9;7:39528. doi: 10.1038/srep39528. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28067243 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of miRNAs and Gastric Cancer: A Scoping Review.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2022 Oct;26(10):459-467. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2021.0258. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2022. PMID: 36251855
-
MicroRNA Changes in Gastric Carcinogenesis: Differential Dysregulation during Helicobacter pylori and EBV Infection.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;12(4):597. doi: 10.3390/genes12040597. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gastric cancer actionable genomic alterations across diverse populations worldwide and pharmacogenomics strategies based on precision oncology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 2;15:1373007. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373007. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38756376 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNA as Biomarkers and Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Gastric Cancer-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5144. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105144. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of USP22 by miR-200b-5p represses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Dec 20;57(6):879-889. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024231. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39711149 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism in the Hsa-miR-4274 seed region influences the expression of PEX5 and enhances radiotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer.Front Med. 2024 Oct;18(5):921-937. doi: 10.1007/s11684-024-1082-6. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 39190270
-
MIR938 rs2505901 T>C polymorphism is associated with increased neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children.Biosci Rep. 2023 Nov 30;43(11):BSR20231223. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231223. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37905791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Today. [(accessed on 23 September 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- Ossandon F.J., Villarroel C., Aguayo F., Santibanez E., Oue N., Yasui W., Corvalán A.H. In silico analysis of gastric carcinoma Serial Analysis of Gene Expression libraries reveals different profiles associated with ethnicity. Mol. Cancer. 2008;7:22. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-22. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

