Infections, Reactions of Natural Killer T Cells and Natural Killer Cells, and Kidney Injury
- PMID: 35008905
- PMCID: PMC8745257
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010479
Infections, Reactions of Natural Killer T Cells and Natural Killer Cells, and Kidney Injury
Abstract
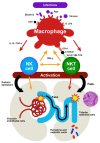
Natural killer T (NKT) cells and NK cells are representative innate immune cells that perform antitumor and antimicrobial functions. The involvement of these cells in various renal diseases, including acute kidney injury (AKI), has recently become evident. Murine NKT cells are activated and cause AKI in response to various stimuli, such as their specific ligand, cytokines, and bacterial components. Both renal vascular endothelial cell injury (via the perforin-mediated pathway) and tubular epithelial cell injury (via the tumor necrosis factor-alpha/Fas ligand pathway) are independently involved in the pathogenesis of AKI. NK cells complement the functions of NKT cells, thereby contributing to the development of infection-associated AKI. Human CD56+ T cells, which are a functional counterpart of murine NKT cells, as well as a subpopulation of CD56+ NK cells, strongly damage intrinsic renal cells in vitro upon their activation, possibly through mechanisms similar to those in mice. These cells are also thought to be involved in the acute exacerbation of pre-existing glomerulonephritis triggered by infection in humans, and their roles in sepsis-associated AKI are currently under investigation. In this review, we will provide an overview of the recent advances in the understanding of the association among infections, NKT and NK cells, and kidney injury, which is much more profound than previously considered. The important role of liver macrophages in the activation of NKT cells will also be introduced.
Keywords: CD56; CD56+ T cell; acute kidney injury; infection; natural killer T cell; natural killer cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

