Stem Cell-Derived β Cells: A Versatile Research Platform to Interrogate the Genetic Basis of β Cell Dysfunction
- PMID: 35008927
- PMCID: PMC8745644
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010501
Stem Cell-Derived β Cells: A Versatile Research Platform to Interrogate the Genetic Basis of β Cell Dysfunction
Abstract
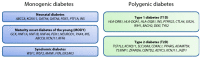
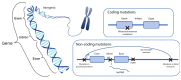
Pancreatic β cell dysfunction is a central component of diabetes progression. During the last decades, the genetic basis of several monogenic forms of diabetes has been recognized. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have also facilitated the identification of common genetic variants associated with an increased risk of diabetes. These studies highlight the importance of impaired β cell function in all forms of diabetes. However, how most of these risk variants confer disease risk, remains unanswered. Understanding the specific contribution of genetic variants and the precise role of their molecular effectors is the next step toward developing treatments that target β cell dysfunction in the era of personalized medicine. Protocols that allow derivation of β cells from pluripotent stem cells, represent a powerful research tool that allows modeling of human development and versatile experimental designs that can be used to shed some light on diabetes pathophysiology. This article reviews different models to study the genetic basis of β cell dysfunction, focusing on the recent advances made possible by stem cell applications in the field of diabetes research.
Keywords: GWAS; SNP; T1D; T2D; beta cell; diabetes; genetic variants; hESC; iPSC; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome Editing Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to Model β-Cell Disease and Unmask Novel Genetic Modifiers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 2;12:682625. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.682625. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34149620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and potential applications of human pluripotent stem cell-derived pancreatic β cells.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020 Jul 10;52(7):708-715. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa047. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020. PMID: 32445468 Review.
-
Genome editing of human pancreatic beta cell models: problems, possibilities and outlook.Diabetologia. 2019 Aug;62(8):1329-1336. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4908-z. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31161346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Genetic Association to Molecular Mechanisms for Islet-cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes.J Mol Biol. 2020 Mar 6;432(5):1551-1578. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.12.045. Epub 2020 Jan 13. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31945378 Review.
-
Modeling different types of diabetes using human pluripotent stem cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2459-2483. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03710-9. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33242105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HNF1A Mutations and Beta Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3222. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063222. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell-Derived Islets for Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 4;23(9):5099. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095099. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

