Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Related Proteins Modified by Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Proteins
- PMID: 35008940
- PMCID: PMC8745615
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010514
Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Related Proteins Modified by Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Proteins
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common form of an acute leukemia, is a malignant disorder of stem cell precursors of the myeloid lineage. Ubiquitination is one of the post-translational modifications (PTMs), and the ubiquitin-like proteins (Ubls; SUMO, NEDD8, and ISG15) play a critical role in various cellular processes, including autophagy, cell-cycle control, DNA repair, signal transduction, and transcription. Also, the importance of Ubls in AML is increasing, with the growing research defining the effect of Ubls in AML. Numerous studies have actively reported that AML-related mutated proteins are linked to Ub and Ubls. The current review discusses the roles of proteins associated with protein ubiquitination, modifications by Ubls in AML, and substrates that can be applied for therapeutic targets in AML.
Keywords: ISGylation; NEDDylation; SUMOylation; deubiquitination; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
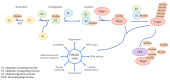
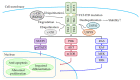
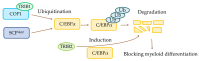
References
-
- Juliusson G., Hough R. Leukemia. Prog. Tumor. Res. 2016;43:87–100. - PubMed
-
- Nishikata I., Sasaki H., Iga M., Tateno Y., Imayoshi S., Asou N., Nakamura T., Morishita K. A novel EVI1 gene family, MEL1, lacking a PR domain (MEL1S) is expressed mainly in t(1;3)(p36;q21)-positive AML and blocks G-CSF-induced myeloid differentiation. Blood. 2003;102:3323–3332. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3944. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

