IL-17 Pathway Members as Potential Biomarkers of Effective Systemic Treatment and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis
- PMID: 35008981
- PMCID: PMC8745093
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010555
IL-17 Pathway Members as Potential Biomarkers of Effective Systemic Treatment and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis
Abstract
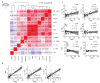
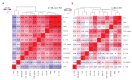
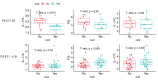
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD). Systemic anti-psoriatic treatments mainly include methotrexate and biological therapies targeting TNF, IL-12/23 and IL-17A. We profiled plasma proteins from patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis to explore potential biomarkers of effective systemic treatment and their relationship to CVD. We found that systemically well-treated patients (PASI < 3.0, n = 36) had lower circulating levels of IL-17 pathway proteins compared to untreated patients (PASI > 10, n = 23). Notably, IL-17C and PI3 were decreased with all four examined systemic treatment types. Furthermore, in patients without CVD, we observed strong correlations among IL-17C/PI3/PASI (r ≥ 0.82, p ≤ 1.5 × 10-12) pairs or between IL-17A/PASI (r = 0.72, p = 9.3 × 10-8). In patients with CVD, the IL-17A/PASI correlation was abolished (r = 0.2, p = 0.24) and the other correlations were decreased, e.g., IL-17C/PI3 (r = 0.61, p = 4.5 × 10-5). Patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis and CVD had lower levels of IL-17A compared to those without CVD (normalized protein expression [NPX] 2.02 vs. 2.55, p = 0.013), and lower IL-17A levels (NPX < 2.3) were associated with higher incidence of CVD (OR = 24.5, p = 0.0028, 95% CI 2.1-1425.1). As a result, in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis, we propose circulating IL-17C and PI3 as potential biomarkers of effective systemic anti-psoriatic treatment, and IL-17A as potential marker of CVD.
Keywords: IL-17A; IL-17C; Olink; PI3/elafin; cardiovascular disease; proteomics; psoriasis; psoriasis area and severity index.
Conflict of interest statement
P.R.H. is recipient of a Borregaard Clinical Scientist Fellowship from the NOVO Nordisk Foundation and chairs a clinical academic group supported by the Greater Region of Copenhagen. C.B. is a consultant for Onegevity Health. L.S. has been a paid speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly and LEO Pharma, and has been a consultant or served on Advisory Boards with AbbVie, Janssen Cilag, Novartis, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, UCB, Admirall and Sanofi. She has served as an investigator for AbbVie, Janssen Cilag, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron and LEO Pharma and received research and educational grant from Pfizer, AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi, Janssen Cilag and Leo Pharma. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
IL-1β, IL-17A and combined phototherapy predicts higher while previous systemic biologic treatment predicts lower treatment response to etanercept in psoriasis patients.Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Feb;27(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0530-9. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Inflammopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30242748
-
Association between serum interleukin-17A and clinical response to tofacitinib and etanercept in moderate to severe psoriasis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018 Oct;43(7):790-797. doi: 10.1111/ced.13561. Epub 2018 May 10. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29748971 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacodynamic Response to Deucravacitinib, an Oral, Selective, Allosteric TYK2 Inhibitor, in a Global, Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Psoriasis Trial.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Oct;14(10):2827-2839. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01262-5. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39283417 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 Links Inflammatory Cross-Talks Between Comorbid Psoriasis and Atherosclerosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 13;13:835671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835671. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35514987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 15;10:3096. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03096. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32010143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Involvement of New Members of the Interleukin Family in Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025;21(4):e1573403X330079. doi: 10.2174/011573403X330079241213071055. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39844544 Review.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Biological Therapies in Very Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Real-Life Retrospective Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Feb 7;14(2):186. doi: 10.3390/jpm14020186. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38392619 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions in cytokine signaling: novel horizons for psoriasis treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 15;16:1573905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1573905. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40303401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Personalized Medicine in Psoriasis: Current Progress.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022 Sep 1;12:231-250. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S328460. eCollection 2022. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 36071793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence of New-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Oral and Gastrointestinal Candidiasis, Herpes Zoster, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, and Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis Exposed to Biologics.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 13;12(24):7653. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247653. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137722 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

