Identification of microRNAs from Medicinal Plant Murraya koenigii by High-Throughput Sequencing and Their Functional Implications in Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis
- PMID: 35009050
- PMCID: PMC8747174
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11010046
Identification of microRNAs from Medicinal Plant Murraya koenigii by High-Throughput Sequencing and Their Functional Implications in Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis
Abstract
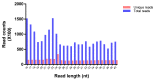
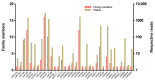
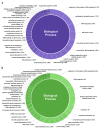
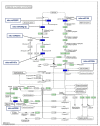
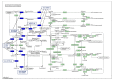
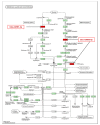
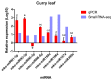
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNA molecules that play crucial post-transcriptional regulatory roles in plants, including development and stress-response signaling. However, information about their involvement in secondary metabolism is still limited. Murraya koenigii is a popular medicinal plant, better known as curry leaves, that possesses pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites. The present study utilized high-throughput sequencing technology to investigate the miRNA profile of M. koenigii and their association with secondary metabolite biosynthesis. A total of 343,505 unique reads with lengths ranging from 16 to 40 nt were obtained from the sequencing data, among which 142 miRNAs were identified as conserved and 7 as novel miRNAs. Moreover, 6078 corresponding potential target genes of M. koenigii miRNAs were recognized in this study. Interestingly, several conserved and novel miRNAs of M. koenigii were found to target key enzymes of the terpenoid backbone and the flavonoid biosynthesis pathways. Furthermore, to validate the sequencing results, the relative expression of eight randomly selected miRNAs was determined by qPCR. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the M. koenigii miRNA profile that may provide useful information for further elucidation of the involvement of miRNAs in secondary metabolism. These findings might be crucial in the future to generate artificial-miRNA-based, genetically engineered M. koenigii plants for the overproduction of medicinally highly valuable secondary metabolites.
Keywords: Illumina sequencing; Murraya koenigii; gene regulation; medicinal plant; microRNA (miRNA); secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) MicroRNAs through Deep Sequencing and Their Impact on Plant Secondary Metabolism.Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 25;12(9):1756. doi: 10.3390/plants12091756. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176813 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) MicroRNAs by Next-Generation Sequencing and Their Implications in Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 8;13(19):2806. doi: 10.3390/plants13192806. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409679 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of conserved and novel microRNAs in one bud and two tender leaves of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) by small RNA sequencing, microarray-based hybridization and genome survey scaffold sequences.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Nov 21;17(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1169-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29157210 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Profile, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Murraya koenigii and its Primary Bioactive Compounds.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jan 24;9(2):101. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020101. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31991665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phyto-Pharmacological Review on Murraya koenigii (L.) Spreng: As an Indigenous Plant of India with High Medicinal Potential.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Jul;20(7):e202300483. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202300483. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 37269458 Review.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Applications of Artificial MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in Plant Biotechnology.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Mar 2;11(2):19. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020019. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Analysis of Physiological, mRNA Sequencing, and miRNA Sequencing Data Reveals a Specific Mechanism for the Response to Continuous Cropping Obstacles in Pogostemon cablin Roots.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 1;13:853110. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.853110. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35432413 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Tuberculosis Epidemiology: Platforms and Approaches for Investigating the Genome's Dark Matter.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 17;23(8):4430. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084430. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Involvement of microRNAs in Plant Lignan Biosynthesis-Current View.Cells. 2022 Jul 8;11(14):2151. doi: 10.3390/cells11142151. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-122 overexpression suppresses the colon cancer cell proliferation by downregulating the astrocyte elevated gene-1/metadherin oncoprotein.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2478311. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2478311. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40208016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chauhan B., Dedania J., Mashru D.R.C. Review on Murraya Koenigii: Versatile Role in Management of Human Health. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017;6:476–493. doi: 10.20959/wjpps20172-8740. - DOI
-
- Nandan S., Singh S.K., Singh P., Bajpai V., Mishra A.K., Joshi T., Mahar R., Shukla S.K., Mishra D.K., Kanojiya S. Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Carbazole Alkaloids in Murraya koenigii (L.) from Six Different Climatic Zones of India Using UPLC/MS/MS and Their Principal Component Analysis. Chem. Biodivers. 2021;18 doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202100557. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gupta P. A review on therapeutic use of Murraya koenigii (L.) Spreng. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020;2:93–97.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

