Enzymatic and Microwave Pretreatments and Supercritical CO2 Extraction for Improving Extraction Efficiency and Quality of Origanum vulgare L. spp. hirtum Extracts
- PMID: 35009059
- PMCID: PMC8747452
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11010054
Enzymatic and Microwave Pretreatments and Supercritical CO2 Extraction for Improving Extraction Efficiency and Quality of Origanum vulgare L. spp. hirtum Extracts
Abstract
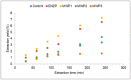
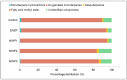
The goal of the study was to establish a procedure for improving the efficiency of supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) extraction of Origanum vulgare L. spp. hirtum (Greek oregano) and enhancing the quality of obtained extracts. Microwave and enzymatic pretreatments of the plant material were applied prior to the scCO2 extraction. It was determined that the microwave pretreatment with irradiation power 360 W during 2 min accelerated the extraction of lipophilic compounds and provided a twofold higher extraction yield compared to the control. Moreover, this pretreatment also led to an increase in oxygenated monoterpenes content and the most dominant component carvacrol, as well as the extracts' antioxidant activity. The enzymatic pretreatment caused a significant increase in the extraction yield and the attainment of the extract with the most potent antioxidant properties. Coupling the pretreatments with scCO2 extraction improves the process of obtaining high value lipophilic products of oregano in terms of utilization of the plant material, acceleration of the extraction with the possibility to adjust its selectivity and quality of extracts, and enhancement of biological activity.
Keywords: Origanum vulgare; enzymatic pretreatment; microwave pretreatment; supercritical carbon dioxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mechergui K., Boukhchina S., Khouja M.L., Coelho J.A., Palavra A.M., Ben Lamine S. Characterisation of supercritical carbon dioxide extract oils from Origanum glandulosum Desf. From two wild Tunisian populations, chemical composition and antioxidant activities. Acta Hortic. 2013;997:83–88. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2013.997.9. - DOI
-
- Simándi B., Oszagyán M., Lemberkovics É., Kéry Á., Kaszács J., Thyrion F., Mátyás T. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and fractionation of oregano oleoresin. Food Res. Int. 1998;31:723–728. doi: 10.1016/S0963-9969(99)00051-4. - DOI
-
- Pezzani R., Vitalini S., Iriti M. Bioactivities of Origanum vulgare L.: An update. Phytochem. Rev. 2017;16:1253–1268. doi: 10.1007/s11101-017-9535-z. - DOI
-
- Ocana-Fuentes A., Arranz-Gutierrez E., Senorans F.J., Reglero G. Supercritical fluid extraction of oregano (Origanum vulgare) essentials oils: Anti-inflammatory properties based on cytokine response on THP-1 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010;48:1568–1575. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.03.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santoyo S., Cavero S., Jaime L., Ibanez E., Senorans F.J., Reglero G. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of compounds with antimicrobial activity from Origanum vulgare L.: Determination of optimal extraction parameters. J. Food Prot. 2006;69:369–375. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-69.2.369. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

