Effect of Salt Stress and Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid on Morphological, Biochemical, Anatomical, and Productivity Characteristics of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) Plants
- PMID: 35009118
- PMCID: PMC8747403
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11010115
Effect of Salt Stress and Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid on Morphological, Biochemical, Anatomical, and Productivity Characteristics of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) Plants
Abstract
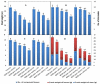
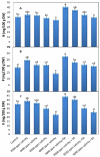
The present study aimed to investigate the impact of salinity on vegetative growth, chemical constituents, and yields of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata) and the possible benefits of salicylic acid (SA) on these plants after damage from salinity. To achieve these objectives, two pot experiments were carried out at the Faculty of Agriculture, Al-Azhar University, Egypt, during the two growing seasons of 2019 and 2020. The results revealed that salinity significantly decreased, and SA treatment substantially increased the plant height, number of compound leaves, number of internodes per plant, fresh weights of leaves and stems, productivity, photosynthetic pigments content, and concentrations of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) of the cowpea plants compared with the control. The anatomical structure of stems and leaves of the plants were also investigated, and it was found that positive variations in the anatomical structure of the median portion of the main stems and blades of mature foliage leaves were detected in the stressed and SA-treated plants. In conclusion, SA treatment increased the salt stress tolerance of cowpea plants by improving the morphological and physiological attributes of the plants.
Keywords: SA; Vigna unguiculata L.; anatomy; growth; photosynthetic pigments; productivity; salinity stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Assessment of selenium spatial distribution using μ-XFR in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) plants: Integration of physiological and biochemical responses.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Jan 1;207:111216. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111216. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 32916525
-
Physiological Responses of Salinized Fenugreek (Trigonellafoenum-graecum L.) Plants to Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid.Plants (Basel). 2021 Mar 30;10(4):657. doi: 10.3390/plants10040657. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33808186 Free PMC article.
-
The Response of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) Plants to Three Abiotic Stresses Applied with Increasing Intensity: Hypoxia, Salinity, and Water Deficit.Metabolites. 2022 Jan 4;12(1):38. doi: 10.3390/metabo12010038. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35050160 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Exogenous Salicylic Acid and Nitric Oxide on Growth, Photosynthesis, and Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle in Salt Stressed Vigna angularis.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 26;10(1):42. doi: 10.3390/biom10010042. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31888108 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of salicylic acid application affects the response of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids to salinity stress.Heliyon. 2019 Apr 28;5(4):e01547. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01547. eCollection 2019 Apr. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31183422 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancing salt stress tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings: insights from trehalose and mannitol.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 30;24(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04964-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38811894 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of morphophysiological and anatomical attributes of plants under abiotic stress conditions using plant growth-promoting bacteria and safety treatments.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 30;12:e17286. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17286. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38708356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing antidiabetic properties of Galega officinalis extract: Investigating the effects of foliar application of chitosan and salicylic acid.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 May 27;12(8):5844-5857. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4204. eCollection 2024 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39139975 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Anatomical Responses of Faba Bean Plants Infected with Chocolate Spot Disease to Chemical Inducers.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;13(2):392. doi: 10.3390/life13020392. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836749 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Potassium Humate and Salicylic Acid to Mitigate Salinity Stress of Common Bean.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 5;13(2):448. doi: 10.3390/life13020448. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halli H.M., Angadi S.S. Influence of land configuration on rain water use efficiency, yield and economics of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) in maize-cowpea sequence cropping under rainfed condition of Northern Transitional Zone. Legume Res. Int. J. 2019;42:211–215. doi: 10.18805/LR-3985. - DOI
-
- Abdel-Azeem A., Nada A.A., O’Donovan A., Kumar Thakur V., Elkelish A. Mycogenic Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Trichoderma Atroviride with Antimicrobial Activity. J. Renew. Mater. 2019;7:171–185. doi: 10.32604/jrm.2020.08960. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

