Flexible Ni/NiOx-Based Sensor for Human Breath Detection
- PMID: 35009195
- PMCID: PMC8746032
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15010047
Flexible Ni/NiOx-Based Sensor for Human Breath Detection
Abstract
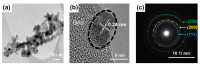
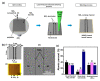
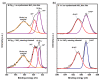
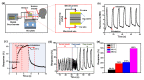
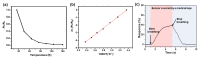
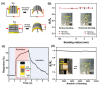
We developed a simple methodology to fabricate an Ni/NiOx-based flexible breath sensor by a single-step laser digital patterning process of solution-processed NiOx thin-film deposited using NiOx nanoparticle ink. Laser-induced reductive sintering phenomenon enables for the generation of three parts of Ni electrodes and two narrow NiOx-sensing channels in between, defined on a single layer on a thin flexible polymer substrate. The Ni/NiOx-based breath sensor efficiently detects human breath at a relatively low operating temperature (50 °C) with fast response/recovery times (1.4 s/1.7 s) and excellent repeatability. The mechanism of the gas-sensing ability enhancement of the sensor was investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. Furthermore, by decoupling of the temperature effect from the breathing gas, the response of the sensor due to the temperature alone and due to the chemical components in the breathing gas could be separately evaluated. Finally, bending and cyclic bending tests (10,000 cycles) demonstrated the superior mechanical stability of the flexible breath sensor.
Keywords: Ni; NiOx; breath sensor; flexible sensor; laser digital patterning; laser-induced reductive sintering process; nanoparticles; nickel; nickel oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bates J., Schmalisch G., Filbrun D., Stocks J. Tidal breath analysis for infant pulmonary function testing. ERS/ATS task force on standards for infant respiratory function testing. European respiratory society/American thoracic society. Eur. Respir. J. 2000;16:1180–1192. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.16f26.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fleischer M., Simon E., Rumpel E., Ulmer H., Harbeck M., Wandel M., Fietzek C., Weimar U., Meixner H. Detection of Volatile Compounds Correlated to Human Diseases Through Breath Analysis with Chemical Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001;83:1746–1749. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59497-7_413. - DOI
-
- Yu J.-B., Byun H.-G., So M.-S., Huh J.-S. Analysis of diabetic patient’s breath with conducting polymer sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005;108:305–308. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.01.040. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

