Electrical Stimulation and Cellular Behaviors in Electric Field in Biomedical Research
- PMID: 35009311
- PMCID: PMC8746014
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15010165
Electrical Stimulation and Cellular Behaviors in Electric Field in Biomedical Research
Abstract
Research on the cellular response to electrical stimulation (ES) and its mechanisms focusing on potential clinic applications has been quietly intensified recently. However, the unconventional nature of this methodology has fertilized a great variety of techniques that make the interpretation and comparison of experimental outcomes complicated. This work reviews more than a hundred publications identified mostly from Medline, categorizes the techniques, and comments on their merits and weaknesses. Electrode-based ES, conductive substrate-mediated ES, and noninvasive stimulation are the three principal categories used in biomedical research and clinic. ES has been found to enhance cell proliferation, growth, migration, and stem cell differentiation, showing an important potential in manipulating cellular activities in both normal and pathological conditions. However, inappropriate parameters or setup can have negative effects. The complexity of the delivered electric signals depends on how they are generated and in what form. It is also difficult to equate one set of parameters with another. Mechanistic studies are rare and badly needed. Even so, ES in combination with advanced materials and nanotechnology is developing a strong footing in biomedical research and regenerative medicine.
Keywords: biophysical stimuli; conductive polymer; electrical stimulation; electrode; in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
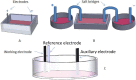


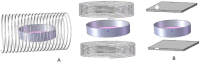
Similar articles
-
Electrical stimulation enhances the acetylcholine receptors available for neuromuscular junction formation.Acta Biomater. 2016 Nov;45:328-339. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27554016
-
Bioelectronics for electrical stimulation: materials, devices and biomedical applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Aug 27;53(17):8632-8712. doi: 10.1039/d4cs00413b. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 39132912 Review.
-
Electrical Stimulation and Conductive Polymers as a Powerful Toolbox for Tailoring Cell Behaviour in vitro.Front Med Technol. 2021 Jul 29;3:670274. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2021.670274. eCollection 2021. Front Med Technol. 2021. PMID: 35047926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural responses to electrical stimulation in 2D and 3D in vitro environments.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Oct;152:265-284. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.07.016. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 31323281 Review.
-
Electrical stimulation affects neural stem cell fate and function in vitro.Exp Neurol. 2019 Sep;319:112963. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.112963. Epub 2019 May 21. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31125549 Review.
Cited by
-
Conducting polymer hydrogels for biomedical application: Current status and outstanding challenges.APL Bioeng. 2024 Sep 24;8(3):031503. doi: 10.1063/5.0218251. eCollection 2024 Sep. APL Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 39323539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foundational insights for theranostic applications of magnetoelectric nanoparticles.Nanoscale Horiz. 2025 Mar 24;10(4):699-718. doi: 10.1039/d4nh00560k. Nanoscale Horiz. 2025. PMID: 39898755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical Stimulation Methods Developed for In Vitro Neuronal Differentiation Studies of PC12 Cells: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 7;25(2):772. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020772. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Cell Culture Chamber for Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Neural Growth.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 26;12(2):289. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020289. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397891 Free PMC article.
-
TECAR Therapy Associated with High-Intensity Laser Therapy (Hilt) and Manual Therapy in the Treatment of Muscle Disorders: A Literature Review on the Theorised Effects Supporting Their Use.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 19;11(20):6149. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206149. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Serena E., Figallo E., Tandon N., Cannizzaro C., Gerecht S., Elvassore N., Vunjak-Novakovic G. Electrical stimulation of human embryonic stem cells: Cardiac differentiation and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Exp. Cell Res. 2009;315:3611–3619. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.08.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

