Effect of Oxalic Acid Treatment on Conductive Coatings Formed by Ni@Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles
- PMID: 35009452
- PMCID: PMC8746183
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15010305
Effect of Oxalic Acid Treatment on Conductive Coatings Formed by Ni@Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Abstract
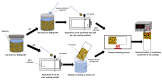
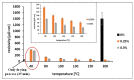
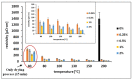
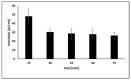
Low-cost metallic nanoink based on nickel-silver core-shell nanoparticles (Ni@Ag NPs) was used for the formation of conductive metallic coatings with low sintering temperature, which can be successfully applied for replacement of currently used silver-based nanoinks in printed electronics. The effect of oxalic acid (OA) on the sintering temperature and conductivity of coatings formed by Ni@Ag NPs was evaluated. It was found that the addition of OA to the ink formulation and post-printing treatment of deposited films with this acid provided a noticeable decrease in the sintering temperature required for obtaining conductive patterns that is especially important for utilizing the polymeric substrates. The obtained resistivity of metallic coatings after sintering at temperature as low as 100 °C was found to be 30 µΩ·cm, only ~4 times higher compared to the resistivity of bulk Ni that is promising for future application of such materials for fabrication of low-cost flexible printed patterns.
Keywords: conductive coatings; conductivity; nickel–silver core–shell nanoparticles; oxalic acid; sintering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Recent Progress on Nickel@Silver Metals Core@Shell Nanoparticles Application in Printed Conductive Materials - A Mini-Review.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025 Apr 14;18:197-210. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S509925. eCollection 2025. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40255991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver Shell Thickness-Dependent Conductivity of Coatings Based on Ni@Ag Core@shell Nanoparticles.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2023 Dec 27;16:73-84. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S435432. eCollection 2023. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2023. PMID: 38161487 Free PMC article.
-
Application of metallic inks based on nickel-silver core-shell nanoparticles for fabrication of conductive films.Nanotechnology. 2019 May 31;30(22):225301. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab0467. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Nanotechnology. 2019. PMID: 30721883
-
Polydispersity vs. Monodispersity. How the Properties of Ni-Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles Affect the Conductivity of Ink Coatings.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;14(9):2304. doi: 10.3390/ma14092304. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946794 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles Based Ink with Moderate Sintering in Flexible and Printed Electronics.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 29;20(9):2124. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092124. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31036787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UV-Vis Sintering Process for Fabrication of Conductive Coatings Based on Ni-Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles.Materials (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;16(22):7218. doi: 10.3390/ma16227218. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005147 Free PMC article.
-
The Recent Progress on Nickel@Silver Metals Core@Shell Nanoparticles Application in Printed Conductive Materials - A Mini-Review.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025 Apr 14;18:197-210. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S509925. eCollection 2025. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40255991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver Shell Thickness-Dependent Conductivity of Coatings Based on Ni@Ag Core@shell Nanoparticles.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2023 Dec 27;16:73-84. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S435432. eCollection 2023. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2023. PMID: 38161487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamyshny A., Magdassi S. Matallic nanoinks for inkjet printing of conductive 2D and 3D structures. In: Kamyshny A., Magdassi S., editors. Nanomaterials for 2D and 3D Printing. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2017. pp. 119–160.
-
- Harris K.D., Elias A.L., Chung H.-J. Flexible electronics under strain: A review of mechanical characterization and durability enhancement strategies. J. Mater. Sci. 2016;51:2771–2805. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9643-3. - DOI
-
- Wünscher S., Abbel R., Perelaer J., Schubert U.S. Progress of alternative sintering approaches of inkjet-printed metal inks and their application for manufacturing of flexible electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2014;2:10232–10261. doi: 10.1039/C4TC01820F. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

