Structural Analysis of Lignin-Based Furan Resin
- PMID: 35009496
- PMCID: PMC8746157
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15010350
Structural Analysis of Lignin-Based Furan Resin
Abstract
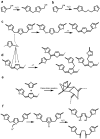
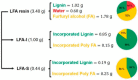
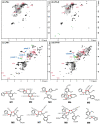
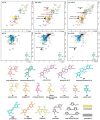
The global "carbon emission peak" and "carbon neutrality" strategic goals promote us to replace current petroleum-based resin products with biomass-based resins. The use of technical lignins and hemicellulose-derived furfuryl alcohol in the production of biomass-based resins are among the most promising ways. Deep understanding of the resulting resin structure is a prerequisite for the optimization of biomass-based resins. Herein, a semiquantitative 2D HSQC NMR technique supplemented by the quantitative 31P NMR and methoxyl group wet chemistry analysis were employed for the structural elucidation of softwood kraft lignin-based furfuryl alcohol resin (LFA). The LFA was fractionated into water-insoluble (LFA-I) and soluble (LFA-S) parts. The analysis of methoxyl groups showed that the amount of lignin was 85 wt% and 44 wt% in LFA-I and LFA-S fractions, respectively. The HSQC spectra revealed the high diversity of linkages formed between lignin and poly FA (pFA). The HSQC and 31P results indicated the formation of new condensed structures, particularly at the 5-position of the aromatic ring. Esterification reactions between carboxyl groups of lignin and hydroxyl groups of pFA could also occur. Furthermore, it was suggested that lignin phenolic hydroxyl oxygen could attack an opened furan ring to form several aryl ethers structures. Therefore, the LFA resin was produced through crosslinking between lignin fragments and pFA chains.
Keywords: NMR; bio-based resin; furfuryl alcohol; lignin; structural analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
New insights into the base catalyzed depolymerization of technical lignins: a systematic comparison.RSC Adv. 2023 Feb 8;13(8):4898-4909. doi: 10.1039/d2ra06998a. eCollection 2023 Feb 6. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36762076 Free PMC article.
-
Demethylation of Alkali Lignin with Halogen Acids and Its Application to Phenolic Resins.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Oct 28;11(11):1771. doi: 10.3390/polym11111771. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31661762 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of technical lignins by two- and three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy.J Agric Food Chem. 2003 Apr 9;51(8):2136-43. doi: 10.1021/jf0204349. J Agric Food Chem. 2003. PMID: 12670147
-
Advances of Modified Lignin as Substitute to Develop Lignin-Based Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Adhesives.ChemSusChem. 2023 Aug 7;16(15):e202300174. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202300174. Epub 2023 Jun 20. ChemSusChem. 2023. PMID: 37338272 Review.
-
Thermosetting Polymers from Lignin Model Compounds and Depolymerized Lignins.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2018 Jul 10;376(4):32. doi: 10.1007/s41061-018-0211-6. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2018. PMID: 29992468 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Variations in Biobased Polyfurfuryl Alcohol Induced by Polymerization in Water.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 31;15(7):1745. doi: 10.3390/polym15071745. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dessbesell L., Paleologou M., Leitch M., Pulkki R., Xu C. Global lignin supply overview and kraft lignin potential as an alternative for petroleum-based polymers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020;123:109768. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.109768. - DOI
-
- Perez R.F., Fraga M.A. Hemicellulose-derived chemicals: One-step production of furfuryl alcohol from xylose. Green Chem. 2014;16:3942–3950. doi: 10.1039/C4GC00398E. - DOI
-
- Gardziella A. Furanharze. In: Woebcken W., editor. Kunststoff-Handbuch. 2nd ed. Volume 10. Carl Hanser Verlag; München, Germany: 1988. pp. 70–84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

