Performance Evaluation of a Voice-Based Depression Assessment System Considering the Number and Type of Input Utterances
- PMID: 35009610
- PMCID: PMC8747535
- DOI: 10.3390/s22010067
Performance Evaluation of a Voice-Based Depression Assessment System Considering the Number and Type of Input Utterances
Abstract
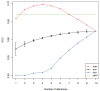
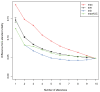
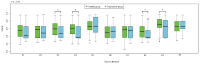
It is empirically known that mood changes affect facial expressions and voices. In this study, the authors have focused on the voice to develop a method for estimating depression in individuals from their voices. A short input voice is ideal for applying the proposed method to a wide range of applications. Therefore, we evaluated this method using multiple input utterances while assuming a unit utterance input. The experimental results revealed that depressive states could be estimated with sufficient accuracy using the smallest number of utterances when positive utterances were included in three to four input utterances.
Keywords: mental health; mood change by positive utterances; voice biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
M.H., M.N. and S.T. had received financial support from PST Inc. until 2019 and currently report no financial support from the company. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
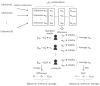
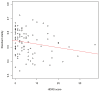
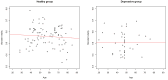
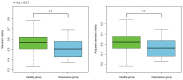
References
-
- Cohen S., Kessler R.C., Gordon L.U. Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1997.
-
- Perkins A. Saving money by reducing stress. Harvard Bus. Rev. 1994;72:12.
-
- Izawa S., Sugaya N., Shirotsuki K., Yamada K.C., Ogawa N., Ouchi Y., Nagano Y., Suzuki K., Nomura S. Salivary dehydroepiandrosterone secretion in response to acute psychosocial stress and its correlations with biological and psychological changes. Biol. Psychol. 2008;79:294–298. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

