A Real-Time Wearable Physiological Monitoring System for Home-Based Healthcare Applications
- PMID: 35009644
- PMCID: PMC8747365
- DOI: 10.3390/s22010104
A Real-Time Wearable Physiological Monitoring System for Home-Based Healthcare Applications
Abstract
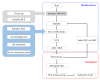
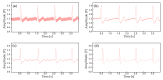
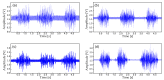
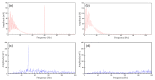
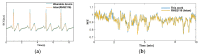
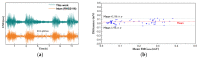
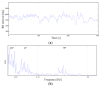
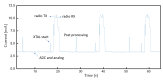
The acquisition of physiological data are essential to efficiently predict and treat cardiac patients before a heart attack occurs and effectively expedite motor recovery after a stroke. This goal can be achieved by using wearable wireless sensor network platforms for real-time healthcare monitoring. In this paper, we present a wireless physiological signal acquisition device and a smartphone-based software platform for real-time data processing and monitor and cloud server access for everyday ECG/EMG signal monitoring. The device is implemented in a compact size (diameter: 30 mm, thickness: 4.5 mm) where the biopotential is measured and wirelessly transmitted to a smartphone or a laptop for real-time monitoring, data recording and analysis. Adaptive digital filtering is applied to eliminate any interference noise that can occur during a regular at-home environment, while minimizing the data process time. The accuracy of ECG and EMG signal coverage is assessed using Bland-Altman analysis by comparing with a reference physiological signal acquisition instrument (RHS2116 Stim/Recording System, Intan). Signal coverage of R-R peak intervals showed almost identical outcome between this proposed work and the RHS2116, showing a mean difference in heart rate of 0.15 ± 4.65 bpm and a Wilcoxon's p value of 0.133. A 24 h continuous recording session of ECG and EMG is conducted to demonstrate the robustness and stability of the device based on extended time wearability on a daily routine.
Keywords: ECG/EMG sensing; physiological monitor; rehabilitation training; smart wearable device; wireless communication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Mozaffarian D., Benjamin E.J., Go A.S., Arnett D.K., Blaha M.J., Cushman M., De Ferranti S., Després J.-P., Fullerton H.J., Howard V.J. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131:e29–e322. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000152. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steinhubl S.R., Waalen J., Edwards A.M., Ariniello L.M., Mehta R.R., Ebner G.S., Carter C., Baca-Motes K., Felicione E., Sarich T. Effect of a home-based wearable continuous ECG monitoring patch on detection of undiagnosed atrial fibrillation: The mSToPS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320:146–155. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.8102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hong S., Kim D., Park H., Seo Y., Hussain I., Park S.J. Gait Feature Vectors for Post-stroke Prediction using Wearable Sensor. Sci. Emot. Sensib. 2019;22:55–64. doi: 10.14695/KJSOS.2018.22.3.55. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

