Preparation and Characterization of a Glycyrrhizic Acid-Based Drug Delivery System for Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy
- PMID: 35010098
- PMCID: PMC8746317
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12010148
Preparation and Characterization of a Glycyrrhizic Acid-Based Drug Delivery System for Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy
Abstract
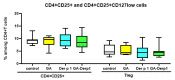
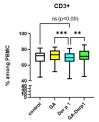
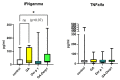
The most effective method of treating allergic diseases, aimed not at relieving symptoms, but at eliminating the cause of the disease, is allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT). To reduce the risk of side effects and improve the delivery of allergens to the mucosa, various delivery systems, such as liposomes, dendrimers, nanoparticles, etc., can be used. To date, there are data on the creation of delivery systems based on glycyrrhizic acid (GA) and its derivatives, but such a delivery system has not been used for allergen-specific therapy until now. It is also known that GA has an anti-inflammatory effect, shifts the balance towards Th1, and increases the number of Treg cells, meaning that it could potentially enhance the anti-allergic effect of AIT and reduce the risk of unwanted side effects. Thus, the study of the immunomodulatory effect of the supramolecular complexes (micelles) of GA with extracts of allergens holds promise for the development of new drugs for AIT.
Keywords: allergen-specific immunotherapy; drug delivery; glycyrrhizic acid; house dust mite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
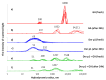
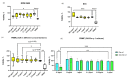
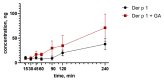
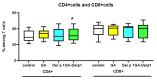
References
-
- Cavone L., Cuppari C., Manti S., Grasso L., Arrigo T., Calamai L., Salpietro C., Chiarugi A. Increase in the Level of Proinflammatory Cytokine HMGB1 in Nasal Fluids of Patients With Rhinitis and its Sequestration by Glycyrrhizin Induces Eosinophil Cell Death. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;8:123–128. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma C., Ma Z., Liao X.L., Liu J., Fu Q., Ma S. Immunoregulatory effects of glycyrrhizic acid exerts anti-asthmatic effects via modulation of Th1/Th2 cytokines and enhancement of CD4(+) CD25(+) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013;148:755–762. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.021. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

