Natural Polymers-Based Materials: A Contribution to a Greener Future
- PMID: 35011326
- PMCID: PMC8747056
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27010094
Natural Polymers-Based Materials: A Contribution to a Greener Future
Abstract
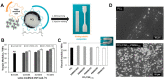
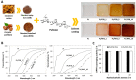
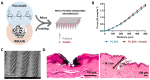
Natural polymers have emerged as promising candidates for the sustainable development of materials in areas ranging from food packaging and biomedicine to energy storage and electronics. In tandem, there is a growing interest in the design of advanced materials devised from naturally abundant and renewable feedstocks, in alignment with the principles of Green Chemistry and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. This review aims to highlight some examples of the research efforts conducted at the Research Team BioPol4fun, Innovation in BioPolymer-based Functional Materials and Bioactive Compounds, from the Portuguese Associate Laboratory CICECO-Aveiro Institute of Materials at the University of Aveiro, regarding the exploitation of natural polymers (and derivatives thereof) for the development of distinct sustainable biobased materials. In particular, focus will be given to the use of polysaccharides (cellulose, chitosan, pullulan, hyaluronic acid, fucoidan, alginate, and agar) and proteins (lysozyme and gelatin) for the assembly of composites, coatings, films, membranes, patches, nanosystems, and microneedles using environmentally friendly strategies, and to address their main domains of application.
Keywords: composites and hybrid materials; films and membranes; green chemistry; microneedles; nanosystems; natural polymers; patches; polysaccharides; proteins; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Yu L., Chen L. Polymeric materials from renewable resources. In: Yu L., editor. Biodegradable Polymer Blends and Composites from Renewable Resources. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2009. pp. 1–15.
-
- El Knidri H., Laajeb A., Lahsini A. Chitin and chitosan: Chemistry, solubility, fiber formation, and their potential applications. In: Gopi S., Thomas S., Pius A., editors. Handbook of Chitin and Chitosan. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. pp. 35–57.
-
- Silvetti T., Morandi S., Hintersteiner M., Brasca M. Use of hen egg white lysozyme in the food industry. In: Hester P.Y., editor. Egg Innovations and Strategies for Improvements. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. pp. 233–242.
-
- Vilela C., Pinto R.J.B., Pinto S., Marques P.A.A.P., Silvestre A.J.D., Freire C.S.R. Polysaccharide Based Hybrid Materials: Metals and Metal Oxides, Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes. 1st ed. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2018. Springer Briefs in Molecular Science.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

