Development of Phenothiazine Hybrids with Potential Medicinal Interest: A Review
- PMID: 35011508
- PMCID: PMC8746661
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27010276
Development of Phenothiazine Hybrids with Potential Medicinal Interest: A Review
Abstract
The molecular hybridization approach has been used to develop compounds with improved efficacy by combining two or more pharmacophores of bioactive scaffolds. In this context, hybridization of various relevant pharmacophores with phenothiazine derivatives has resulted in pertinent compounds with diverse biological activities, interacting with specific or multiple targets. In fact, the development of new drugs or drug candidates based on phenothiazine system has been a promising approach due to the diverse activities associated with this tricyclic system, traditionally present in compounds with antipsychotic, antihistaminic and antimuscarinic effects. Actually, the pharmacological actions of phenothiazine hybrids include promising antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, analgesic and multi-drug resistance reversal properties. The present review summarizes the progress in the development of phenothiazine hybrids and their biological activity.
Keywords: anti-Alzheimer; antimicrobial; antitumor; molecular hybridization; pharmacophore; phenothiazine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



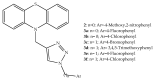


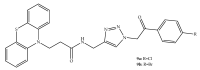
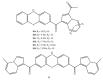



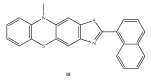











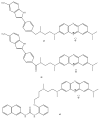


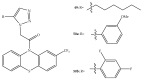





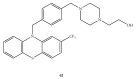
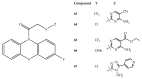
References
-
- Fink D.M., Palermo M.G., Bores G.M., Huger F.P., Kurys B.E., Merriman M.C., Olsen G.E., Petko W., O’Malley G.J. Imino 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocyclopent[b]indole carbamates as Dual Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996;6:625–630. doi: 10.1016/0960-894X(96)00072-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

