KANPHOS: A Database of Kinase-Associated Neural Protein Phosphorylation in the Brain
- PMID: 35011609
- PMCID: PMC8750479
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11010047
KANPHOS: A Database of Kinase-Associated Neural Protein Phosphorylation in the Brain
Abstract
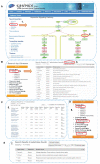
Protein phosphorylation plays critical roles in a variety of intracellular signaling pathways and physiological functions that are controlled by neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the brain. Dysregulation of these signaling pathways has been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and schizophrenia. While recent advances in mass spectrometry-based proteomics have allowed us to identify approximately 280,000 phosphorylation sites, it remains largely unknown which sites are phosphorylated by which kinases. To overcome this issue, previously, we developed methods for comprehensive screening of the target substrates of given kinases, such as PKA and Rho-kinase, upon stimulation by extracellular signals and identified many candidate substrates for specific kinases and their phosphorylation sites. Here, we developed a novel online database to provide information about the phosphorylation signals identified by our methods, as well as those previously reported in the literature. The "KANPHOS" (Kinase-Associated Neural Phospho-Signaling) database and its web portal were built based on a next-generation XooNIps neuroinformatics tool. To explore the functionality of the KANPHOS database, we obtained phosphoproteomics data for adenosine-A2A-receptor signaling and its downstream MAPK-mediated signaling in the striatum/nucleus accumbens, registered them in KANPHOS, and analyzed the related pathways.
Keywords: KANPHOS; adenosine signaling; intellectual disability; molecular mechanism; neurodevelopmental disorders; phosphoproteomics; phosphorylation; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP18dm0207005, JP21dm0207075, JP21wm0425017 and JP21wm0425008/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP16K18393, JP17H01380, JP17K07383, JP17H02220, JP17K19483, JP18K14849, JP19K16370, JP21K06428 and JP21K06427/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP17H05561, JP19H05209 and JP21H00196/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

