Evaluation of Endothelial Dysfunction and Autophagy in Fibromyalgia-Related Vascular and Cerebral Cortical Changes and the Ameliorative Effect of Fisetin
- PMID: 35011610
- PMCID: PMC8750434
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11010048
Evaluation of Endothelial Dysfunction and Autophagy in Fibromyalgia-Related Vascular and Cerebral Cortical Changes and the Ameliorative Effect of Fisetin
Abstract
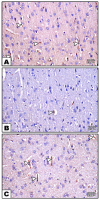
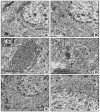
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a common chronic pain syndrome that affects 1% to 5% of the population. We aimed to investigate the role of endothelial dysfunction and autophagy in fibromyalgia-related vascular and cerebral cortical changes in a reserpine-induced rat model of fibromyalgia at the histological and molecular levels and to study the ameliorative effect of fisetin. Forty adult female albino rats were divided into four groups (10 each): two control groups, the reserpine-induced fibromyalgia group, and the fisetin-treated group. The carotid arteries and brains of the animals were dissected. Frozen tissue samples were used for total RNA extraction and qPCR analysis of eNOS, caspase-3, Bcl-2, LC-3, BECN-1, CHOP, and TNF-α expression. Histological, immunohistochemical (eNOS), and ultrastructure studies were conducted. The carotid arteries revealed excessive autophagy and endothelial, vascular, and apoptotic changes. The cerebral cortex showed similar findings apart from endoplasmic reticulum stress. Additionally, there was decreased gene expression of eNOS and Bcl-2 and increased expression of caspase-3, LC-3, BECN-1, CHOP, and TNF-α. In the fisetin-treated rats, improvements in the histological and molecular results were detected. In conclusion, oxidative stress, enhanced apoptosis, and excessive autophagy are fundamental pathophysiologic mechanisms of reserpine-induced fibromyalgia. Moreover, fisetin has an ameliorative effect against fibromyalgia.
Keywords: autophagy; endothelial dysfunction; fibromyalgia; fisetin; reserpine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
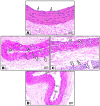
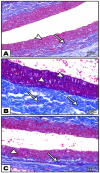
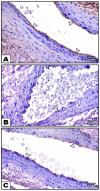

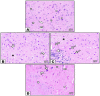
References
-
- Jones G.T., Atzeni F., Beasley M., Flu B.E., Sarzi-Puttini P., Macfarlane G.J. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the general population: A comparison of the American College of Rheumatology 1990, 2010, and modified 2010 classification criteria. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:568–575. doi: 10.1002/art.38905. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Son C.N., Kim S.H., Chang H.W., Kim J.M. A neurometabolite study of chronic daily headache in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus using magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Comparison with fibromyalgia patients and healthy controls. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016;31:1171–1177. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2015.196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

