The RNA-Binding Protein Musashi1 Regulates a Network of Cell Cycle Genes in Group 4 Medulloblastoma
- PMID: 35011618
- PMCID: PMC8750343
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11010056
The RNA-Binding Protein Musashi1 Regulates a Network of Cell Cycle Genes in Group 4 Medulloblastoma
Abstract
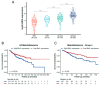
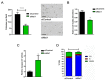
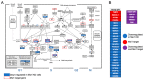
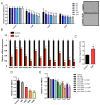
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. Treatment with surgery, irradiation, and chemotherapy has improved survival in recent years, but patients are frequently left with devastating neurocognitive and other sequelae. Patients in molecular subgroups 3 and 4 still experience a high mortality rate. To identify new pathways contributing to medulloblastoma development and create new routes for therapy, we have been studying oncogenic RNA-binding proteins. We defined Musashi1 (Msi1) as one of the main drivers of medulloblastoma development. The high expression of Msi1 is prevalent in Group 4 and correlates with poor prognosis while its knockdown disrupted cancer-relevant phenotypes. Genomic analyses (RNA-seq and RIP-seq) indicated that cell cycle and division are the main biological categories regulated by Msi1 in Group 4 medulloblastoma. The most prominent Msi1 targets include CDK2, CDK6, CCND1, CDKN2A, and CCNA1. The inhibition of Msi1 with luteolin affected the growth of CHLA-01 and CHLA-01R Group 4 medulloblastoma cells and a synergistic effect was observed when luteolin and the mitosis inhibitor, vincristine, were combined. These findings indicate that a combined therapeutic strategy (Msi1 + cell cycle/division inhibitors) could work as an alternative to treat Group 4 medulloblastoma.
Keywords: Musashi1; RNA-binding protein; cell cycle regulation; luteolin; medulloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kieffer V., Chevignard M.P., Dellatolas G., Puget S., Dhermain F., Grill J., Valteau-Couanet D., Dufour C. Intellectual, educational, and situation-based social outcome in adult survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2019;22:19–26. doi: 10.1080/17518423.2018.1424262. - DOI - PubMed
-
- King A.A., Seidel K., Di C., Leisenring W.M., Perkins S.M., Krull K.R., Sklar C.A., Green D.M., Armstrong G.T., Zeltzer L.K., et al. Long-term neurologic health and psychosocial function of adult survivors of childhood medulloblastoma/PNET: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Neuro Oncol. 2017;19:689–698. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now242. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

