COVID-19 Patient Management in Outpatient Setting: A Population-Based Study from Southern Italy
- PMID: 35011810
- PMCID: PMC8745524
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11010051
COVID-19 Patient Management in Outpatient Setting: A Population-Based Study from Southern Italy
Abstract
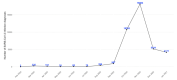
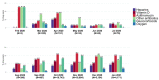
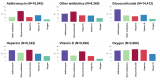
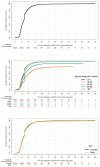
Evidence on treatments for early-stage COVID-19 in outpatient setting is sparse. We explored the pattern of use of drugs prescribed for COVID-19 outpatients' management in Southern Italy in the period February 2020-January 2021. This population-based cohort study was conducted using COVID-19 surveillance registry from Caserta Local Health Unit, which was linked to claims databases from the same catchment area. The date of SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis was the index date (ID). We evaluated demographic and clinical characteristics of the study drug users and the pattern of use of drugs prescribed for outpatient COVID-19 management. Overall, 40,030 patients were included in the analyses, with a median (IQR) age of 44 (27-58) years. More than half of the included patients were asymptomatic at the ID. Overall, during the study period, 720 (1.8%) patients died due to COVID-19. Azithromycin and glucocorticoids were the most frequently prescribed drugs, while oxygen was the less frequently prescribed therapy. The cumulative rate of recovery from COVID-19 was 84.2% at 30 days from ID and it was lower among older patients. In this study we documented that the drug prescribing patterns for COVID-19 treatment in an outpatient setting from Southern Italy was not supported from current evidence on beneficial therapies for early treatment of COVID-19, thus highlighting the need to implement strategies for improving appropriate drug prescribing in general practice.
Keywords: COVID-19; Italy; outpatients.
Conflict of interest statement
In the last 3 years, Gianluca Trifirò has served on advisory boards/seminars funded by several pharmaceutical companies; he was the scientific director of a Master program on pharmacovigilance, pharmacoepidemiology, and real-world evidence at University of Messina, which received non-conditional grants from various pharmaceutical companies; he coordinated a pharmacoepidemiology team at the University of Messina until October 2020, which received funding for conducting observational studies from various pharmaceutical companies; he is also a scientific coordinator of the academic spin-off “INSPIRE srl”, which received funding for conducting observational studies from contract research organizations (RTI Health Solutions, Pharmo Institute N.V.), based on funding from pharmaceutical companies. None of these listed activities are related to the topic of the manuscript. The other authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Food and Drug Administration FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19. [(accessed on 5 November 2021)];2020 Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19....
-
- Food and Drug Administration FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19. [(accessed on 5 November 2021)];2021 Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19....
-
- Food and Drug Administration FDA Authorizes Additional Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19. [(accessed on 5 November 2021)];2021 Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19....
-
- Fischer W.A., Eron J.J., Holman W., Cohen M.S., Fang L., Szewczyk L.J., Sheahan T.P., Baric R.S., Mollan K.R., Wolfe C.R., et al. Molnupiravir, an Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

