Association between Non-HDL-C/HDL-C Ratio and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Post-Menopausal Women
- PMID: 35011818
- PMCID: PMC8745439
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11010078
Association between Non-HDL-C/HDL-C Ratio and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Post-Menopausal Women
Abstract
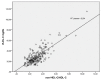
Atherogenic lipoproteins (particularly, very low-density lipoproteins, VLDL) are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis. The present study aims at evaluating whether routinely analysed lipid parameters are associated with carotid intima-media thickness, a proxy for subclinical atherosclerosis. Lipid parameters from 220 post-menopausal women undergoing ultrasound investigation of the carotid arteries were analysed. Forty-five percent of women showed subclinical atherosclerosis on carotid ultrasound. The mean carotid intima-media thickness was 1.26 ± 0.38 mm. The mean value of the non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio was 3.1 ± 1.2. Univariate analysis showed a significant association between non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio and intima-media thickness (r = 0.21, p = 0.001). After adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors (age, systolic blood pressure, smoking, body mass index Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and high-sensitivity C-Reactive-Protein), multivariate analysis showed a significant association between non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio and intima-media thickness (β = 0.039, p = 0.04). Logistic regression analysis showed that the highest tertile of the non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio was associated with the presence of carotid plaques (OR = 3.47, p = 0.003). Finally, a strong correlation between non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio and cholesterol bound to VLDL (r = 0.77, p < 0.001) has been found. Non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio is associated with the presence of carotid atherosclerosis in post-menopausal women and is strongly correlated to VLDL-C levels.
Keywords: carotid intima-media thichness; non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratio; post-menopausal women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Borén J., Chapman M.J., Krauss R.M., Packard C.J., Bentzon J.F., Binder C.J., Daemen M.J., Demer L.L., Hegele R.A., Nicholls S.J., et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2020;41:2313–2330. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gentile M., Iannuzzi A., Iannuzzo G., Covetti G., Panico S., Mattiello A., De Michele M., Rubba P. Relation of body mass index with carotid intima-media thickness and diameter is independent of metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal Mediterranean women. Menopause. 2012;19:1104–1108. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e31825ad66c. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials