Formulation Development, Characterization and Antifungal Evaluation of Chitosan NPs for Topical Delivery of Voriconazole In Vitro and Ex Vivo
- PMID: 35012154
- PMCID: PMC8747354
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14010135
Formulation Development, Characterization and Antifungal Evaluation of Chitosan NPs for Topical Delivery of Voriconazole In Vitro and Ex Vivo
Abstract
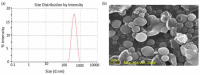
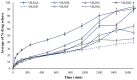
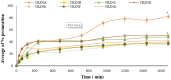
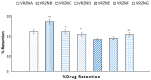
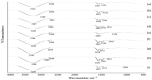
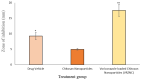
This study aims to develop chitosan-based voriconazole nanoparticles (NPs) using spray-drying technique. The effect of surfactants and polymers on the physicochemical properties, in vitro release, and permeation of NPs was investigated. The prepared NPs containing various surfactants and polymers (e.g., Tween 20 (T20), Tween 80 (T80), sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), propylene glycol (PG), and Polyethylene glycol-4000 (PEG-4000)) were physiochemically evaluated for size, zeta potential, drug content, percent entrapment efficiency, in vitro release, and permeation across rats' skin. A Franz diffusion cell was used for evaluating the in vitro release and permeation profile. The voriconazole-loaded NPs were investigated for antifungal activity against Candida albicans (C. albicans). The prepared NPs were in the nano range (i.e., 160-500 nm) and positively charged. Images taken by a scanning electron microscope showed that all prepared NPs were spherical and smooth. The drug content of NPs ranged from 75% to 90%. Nanoparticle formulations exhibited a good in vitro release profile and transport voriconazole across the rat's skin in a slow control release manner. The NPs containing SLS, T80, and PG exhibited the best penetration and skin retention profile. In addition, the formulation exhibited a potential antifungal effect against C. albicans. It was concluded that the development of chitosan NPs has a great potential for the topical delivery of voriconazole against fungal infection.
Keywords: PEG-4000; PG; chitosan; polymers; topical delivery; voriconazole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Chitosan-Gelatin Thermosensitive Hydrogels Containing 5FU-Alginate Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery.Gels. 2022 Aug 26;8(9):537. doi: 10.3390/gels8090537. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36135249 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Coated 5-Fluorouracil Incorporated Emulsions as Transdermal Drug Delivery Matrices.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;13(19):3345. doi: 10.3390/polym13193345. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641162 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel biopolymer-based nanoparticles loaded cream for potential treatment of topical fungal infections.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021 Jul;47(7):1090-1099. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2021.1957914. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34279160
-
Statistical optimization of voriconazole nanoparticles loaded carboxymethyl chitosan-poloxamer based in situ gel for ocular delivery: In vitro, ex vivo, and toxicity assessment.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Dec;12(12):3063-3082. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01171-0. Epub 2022 May 7. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35525868
-
Nanosuspension as an Efficient Carrier for Improved Ocular Permeation of Voriconazole.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(2):245-253. doi: 10.2174/1389201021999200820154918. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 32867650
Cited by
-
Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery.Gels. 2022 Dec 22;9(1):3. doi: 10.3390/gels9010003. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36661771 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Chitosan-Gelatin Thermosensitive Hydrogels Containing 5FU-Alginate Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery.Gels. 2022 Aug 26;8(9):537. doi: 10.3390/gels8090537. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36135249 Free PMC article.
-
Novasomes as Nano-Vesicular Carriers to Enhance Topical Delivery of Fluconazole: A New Approach to Treat Fungal Infections.Molecules. 2022 May 4;27(9):2936. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092936. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566287 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of Sahasthara Thai medicine remedy in a film-forming spray for topical anti-inflammatory therapy.Res Pharm Sci. 2025 Feb 20;20(1):25-40. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_22_24. eCollection 2025 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40190822 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of Chitosan Formulations in Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10975. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810975. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qurt M.S., Esentürk İ., Tan S.B., Erdal M.S., Araman A., Güngör S. Voriconazole and sertaconazole loaded colloidal nano-carriers for enhanced skin deposition and improved topical fungal treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018;48:215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2018.09.020. - DOI
-
- Latif M.S., Azad A.K., Nawaz A., Rashid S.A., Rahman M., Al Omar S.Y., Bungau S.G., Aleya L., Abdel-Daim M.M. Ethyl Cellulose and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Blended Methotrexate-Loaded Transdermal Patches: In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Polymers. 2021;13:3455. doi: 10.3390/polym13203455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

