[Combined detection of Helicobacter pylori 16S rRNA and cagA gene in saliva specimens using multiplex PCR]
- PMID: 35012913
- PMCID: PMC8752427
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.12.09
[Combined detection of Helicobacter pylori 16S rRNA and cagA gene in saliva specimens using multiplex PCR]
Abstract
Objective: To establish a multiplex PCR-based method for detecting Helicobacter pylori (Hp) 16S rRNA gene and cagA gene in saliva samples for investigating the prevalence of Hp in the oral cavity of Hp-infected patients with digestive tract diseases.
Methods: Bioinformatics technique was used to design specific primers for Hp 16S rRNA and cagA genes for Hp detection using multiplex PCR, with recombinant cloning plasmids serving as the standard positive control. Oral saliva samples were collected from 156 patients with digestive tract diseases, and Hp 16S rRNA and cagA genes were detected using the established multiplex PCR system.
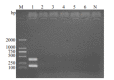
Results: The established multiplex PCR system showed a strong specificity and a high sensitivity for detecting Hp 16S rRNA gene and cagA gene, with the lowest detection limit of 103 copies/μL. The recombinant plasmids pGMT-16s and pGMT-cagA could be used as standard positive controls for the identification of Hp. Among the 156 saliva samples, 87.2% were positive for Hp 16S rRNA gene and 23.1% for Hp cagA gene.
Conclusion: Hp is highly prevalent in saliva specimens of Hp-infected patients with digestive tract diseases. The presence of Hp in the oral cavity may importantly contribute to Hp infection in the digestive tract and recurrence after treatment.
目的: 检测唾液标本幽门螺杆菌(Hp)的16S rRNA基因及cagA基因,了解消化道疾病患者口腔中Hp存在情况及致病情况。
方法: 利用生物学信息技术,设计Hp 16SrRNA、cagA基因特异性引物,建立检测Hp 16SrRNA、cagA基因的多重PCR方法;重组克隆质粒构建标准阳性对照品;收集156例消化道疾病患者的唾液标本,提取唾液标本中细菌DNA,应用建立的多重PCR方法,检测Hp 16SrRNA基因及cagA基因,并对结果进行分析。
结果: 建立的检测Hp 16SrRNA基因及cagA基因的多重PCR方法特异性强,灵敏性较高,最低检测线为103 copies·μL-1;重组质粒pGMT-16s和pGMT-cagA,可作为鉴定Hp的标准阳性对照品;检测Hp感染的消化道疾病患者的唾液标本,口腔携带Hp 16SrRNA基因的阳性率为87.2%,cagA基因阳性率为23.1%。
结论: Hp感染的消化道疾病患者口腔唾液标本中存在Hp,口腔中存在Hp可能是诱发消化道Hp感染及治疗后复发的一个重要原因。
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; Helicobacter pylori; cagA gene; saliva.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Detection of Helicobacter pylori gene expression in human gastric mucosa.J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Jan;33(1):28-32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.1.28-32.1995. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7699060 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species DNA in human bile samples from patients with various hepato-biliary diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Apr 14;12(14):2181-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2181. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16610018 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of cytotoxin genotypes of Helicobacter pylori in stomach, saliva and dental plaque.Arch Oral Biol. 2009 Jul;54(7):684-8. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 May 13. Arch Oral Biol. 2009. PMID: 19442963
-
Detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA in feces and saliva by polymerase chain reaction: a review.Helicobacter. 2004 Apr;9(2):115-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1083-4389.2004.00207.x. Helicobacter. 2004. PMID: 15068412 Review.
-
DNA diagnostics for reliable and universal identification of Helicobacter pylori.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Nov 7;27(41):7100-7112. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7100. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34887630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Viable Bacteria Assay of Helicobacter pylori by RT-qPCR Measurement of cgt Gene Expression Levels: Establishment and Application of a New Method].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Sep 20;55(5):1316-1321. doi: 10.12182/20240960402. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39507989 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Usefulness of Molecular Methods for Helicobacter pylori Detection in Pediatric Patients and Their Correlation with Histopathological Sydney Classification.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 22;24(1):179. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010179. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Snaith A, El-Omar EM. Helicobacter pylori: host genetics and disease outcomes. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2(4):577–85. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2.4.577. [Snaith A, El-Omar EM. Helicobacter pylori: host genetics and disease outcomes[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 2(4): 577-85.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuipers EJ. Helicobacter pylori and the risk and management of associated diseases: gastritis, ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;11(Suppl 1):71–88. [Kuipers EJ. Helicobacter pylori and the risk and management of associated diseases: gastritis, ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 1997, 11(Suppl 1): 71-88.] - PubMed
-
- Wei X, Zhao HQ, Ma C, et al. The association between chronic periodontitis and oral Helicobacter pylori: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0225247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225247. [Wei X, Zhao HQ, Ma C, et al. The association between chronic periodontitis and oral Helicobacter pylori: a meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0225247.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee YC, Chiang TH, Chou CK, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori eradication and gastric cancer incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(5):1113–24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.028. [Lee YC, Chiang TH, Chou CK, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori eradication and gastric cancer incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(5): 1113-24.] - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
