Progranulin mediates immune evasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through regulation of MHCI expression
- PMID: 35013174
- PMCID: PMC8748938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27088-9
Progranulin mediates immune evasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through regulation of MHCI expression
Abstract
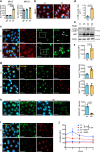
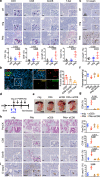
Immune evasion is indispensable for cancer initiation and progression, although its underlying mechanisms in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) are not fully known. Here, we characterize the function of tumor-derived PGRN in promoting immune evasion in primary PDAC. Tumor- but not macrophage-derived PGRN is associated with poor overall survival in PDAC. Multiplex immunohistochemistry shows low MHC class I (MHCI) expression and lack of CD8+ T cell infiltration in PGRN-high tumors. Inhibition of PGRN abrogates autophagy-dependent MHCI degradation and restores MHCI expression on PDAC cells. Antibody-based blockade of PGRN in a PDAC mouse model remarkably decelerates tumor initiation and progression. Notably, tumors expressing LCMV-gp33 as a model antigen are sensitized to gp33-TCR transgenic T cell-mediated cytotoxicity upon PGRN blockade. Overall, our study shows a crucial function of tumor-derived PGRN in regulating immunogenicity of primary PDAC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.T.S. reports the following disclosures: Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Roche (Research Funding); AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Immunocore, Novartis, Roche, Shire (Consulting or advisory role); AstraZeneca, Aurikamed, Baxalta, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Falk Foundation, iomedico, Immunocore, Novartis, Roche, Shire (honoraria); minor equity in iTheranostics and Pharma15 (<3%); member of the Board of Directors for Pharma15, all outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Cheung ST, Cheung PF, Cheng CK, Wong NC, Fan ST. Granulin-epithelin precursor and ATP-dependent binding cassette (ABC)B5 regulate liver cancer cell chemoresistance. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:344–355. - PubMed
-
- Cheung ST, et al. Granulin-epithelin precursor overexpression promotes growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004;10:7629–7636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

