A star-nose-like tactile-olfactory bionic sensing array for robust object recognition in non-visual environments
- PMID: 35013205
- PMCID: PMC8748716
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27672-z
A star-nose-like tactile-olfactory bionic sensing array for robust object recognition in non-visual environments
Abstract
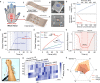
Object recognition is among the basic survival skills of human beings and other animals. To date, artificial intelligence (AI) assisted high-performance object recognition is primarily visual-based, empowered by the rapid development of sensing and computational capabilities. Here, we report a tactile-olfactory sensing array, which was inspired by the natural sense-fusion system of star-nose mole, and can permit real-time acquisition of the local topography, stiffness, and odor of a variety of objects without visual input. The tactile-olfactory information is processed by a bioinspired olfactory-tactile associated machine-learning algorithm, essentially mimicking the biological fusion procedures in the neural system of the star-nose mole. Aiming to achieve human identification during rescue missions in challenging environments such as dark or buried scenarios, our tactile-olfactory intelligent sensing system could classify 11 typical objects with an accuracy of 96.9% in a simulated rescue scenario at a fire department test site. The tactile-olfactory bionic sensing system required no visual input and showed superior tolerance to environmental interference, highlighting its great potential for robust object recognition in difficult environments where other methods fall short.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rudovic O, Lee J, Dai M, Schuller B, Picard RW. Personalized machine learning for robot perception of affect and engagement in autism therapy. Sci. Robot. 2018;3:eaao6760. - PubMed
-
- Ficuciello F, Migliozzi A, Laudante G, Falco P, Siciliano B. Vision-based grasp learning of an anthropomorphic hand-arm system in a synergy-based control framework. Sci. Robot. 2019;4:eaao4900. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Liu S, Wang L, Zhu R. Skin-inspired quadruple tactile sensors integrated on a robot hand enable object recognition. Sci. Robot. 2020;5:eabc8134. - PubMed
-
- Hill MQ, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks in the face of caricature. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019;1:522–529.
-
- Wang M, et al. Gesture recognition using a bioinspired learning architecture that integrates visual data with somatosensory data from stretchable sensors. Nat. Electron. 2020;3:563–570.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

