Robust and durable serological response following pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 35013206
- PMCID: PMC8748910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27595-9
Robust and durable serological response following pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
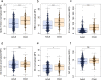
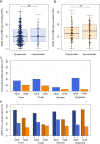
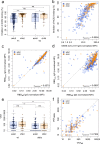
The quality and persistence of children's humoral immune response following SARS-CoV-2 infection remains largely unknown but will be crucial to guide pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccination programs. Here, we examine 548 children and 717 adults within 328 households with at least one member with a previous laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. We assess serological response at 3-4 months and 11-12 months after infection using a bead-based multiplex immunoassay for 23 human coronavirus antigens including SARS-CoV-2 and its Variants of Concern (VOC) and endemic human coronaviruses (HCoVs), and additionally by three commercial SARS-CoV-2 antibody assays. Neutralization against wild type SARS-CoV-2 and the Delta VOC are analysed in a pseudotyped virus assay. Children, compared to adults, are five times more likely to be asymptomatic, and have higher specific antibody levels which persist longer (96.2% versus 82.9% still seropositive 11-12 months post infection). Of note, symptomatic and asymptomatic infections induce similar humoral responses in all age groups. SARS-CoV-2 infection occurs independent of HCoV serostatus. Neutralization responses of children and adults are similar, although neutralization is reduced for both against the Delta VOC. Overall, the long-term humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children is of longer duration than in adults even after asymptomatic infection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.S.M. was a speaker at Luminex user meetings in the past. The Natural and Medical Sciences Institute at the University of Tübingen is involved in applied research projects as a fee for services with Luminex. The other authors report no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

