Deep convolutional neural network-based classification of cancer cells on cytological pleural effusion images
- PMID: 35013527
- PMCID: PMC9042694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41379-021-00987-4
Deep convolutional neural network-based classification of cancer cells on cytological pleural effusion images
Abstract
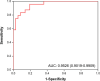
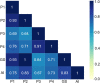
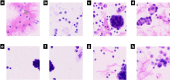
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide. Cytology plays an important role in the initial evaluation and diagnosis of patients with lung cancer. However, due to the subjectivity of cytopathologists and the region-dependent diagnostic levels, the low consistency of liquid-based cytological diagnosis results in certain proportions of misdiagnoses and missed diagnoses. In this study, we performed a weakly supervised deep learning method for the classification of benign and malignant cells in lung cytological images through a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN). A total of 404 cases of lung cancer cells in effusion cytology specimens from Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital were investigated, in which 266, 78, and 60 cases were used as the training, validation and test sets, respectively. The proposed method was evaluated on 60 whole-slide images (WSIs) of lung cancer pleural effusion specimens. This study showed that the method had an accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity respectively of 91.67%, 87.50% and 94.44% in classifying malignant and benign lesions (or normal). The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) was 0.9526 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.9019-9.9909). In contrast, the average accuracies of senior and junior cytopathologists were 98.34% and 83.34%, respectively. The proposed deep learning method will be useful and may assist pathologists with different levels of experience in the diagnosis of cancer cells on cytological pleural effusion images in the future.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare. I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Figures


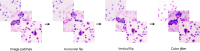
References
-
- Sermanet P, et al. Overfeat: Integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. arXiv. 2014;1312:6229.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

