Partitioning RNAs by length improves transcriptome reconstruction from short-read RNA-seq data
- PMID: 35013600
- PMCID: PMC11332977
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-01136-7
Partitioning RNAs by length improves transcriptome reconstruction from short-read RNA-seq data
Abstract
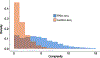
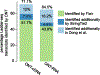
The accuracy of methods for assembling transcripts from short-read RNA sequencing data is limited by the lack of long-range information. Here we introduce Ladder-seq, an approach that separates transcripts according to their lengths before sequencing and uses the additional information to improve the quantification and assembly of transcripts. Using simulated data, we show that a kallisto algorithm extended to process Ladder-seq data quantifies transcripts of complex genes with substantially higher accuracy than conventional kallisto. For reference-based assembly, a tailored scheme based on the StringTie2 algorithm reconstructs a single transcript with 30.8% higher precision than its conventional counterpart and is more than 30% more sensitive for complex genes. For de novo assembly, a similar scheme based on the Trinity algorithm correctly assembles 78% more transcripts than conventional Trinity while improving precision by 78%. In experimental data, Ladder-seq reveals 40% more genes harboring isoform switches compared to conventional RNA sequencing and unveils widespread changes in isoform usage upon m6A depletion by Mettl14 knockout.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
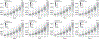

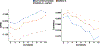




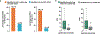

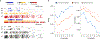
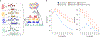
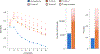

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

