Caveolin-1 Scaffolding Domain Peptide Regulates Colon Endothelial Cell Survival through JNK Pathway
- PMID: 35013693
- PMCID: PMC8742180
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6150942
Caveolin-1 Scaffolding Domain Peptide Regulates Colon Endothelial Cell Survival through JNK Pathway
Abstract
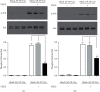
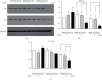
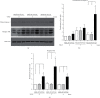
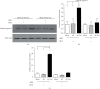
It has been reported that pathological angiogenesis contributes to both experimental colitis and inflammatory bowel disease. Recently, we demonstrated that endothelial caveolin-1 plays a key role in the pathological angiogenesis of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) colitis. However, the molecular mechanism of caveolin-1 regulation of endothelial function is unknown. In this study, we examined how the antennapedia- (AP-) conjugated caveolin-1 scaffolding domain (AP-Cav) modulates vascular endothelial growth factor- (VEGF-) dependent colon endothelial cell angiogenic responses, as seen during colitis. We used mouse colon endothelial cells and found that AP-Cav significantly inhibited VEGF-mediated bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation into colon microvascular endothelial cells. AP-Cav significantly blunted VEGF-dependent extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK 1/2) phosphorylation at 10 minutes and 2 hours after stimulation, compared with the AP control peptide. AP-Cav + VEGF-A treatment also significantly increased c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation at 2 hours. AP-Cav + VEGF-A treatment significantly downregulated retinoblastoma (Rb) protein levels, upregulated cleaved caspase-3 protein levels at 4 hours, and induced apoptosis. Thus, our study suggests that disruption of endothelial caveolin-1 function via the AP-Cav diverts VEGF signaling responses away from endothelial cell proliferation and toward apoptosis through the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling and the induction of JNK-associated apoptosis.
Copyright © 2020 Kai Fang and Christopher G. Kevil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric oxygen induces VEGF expression through ERK, JNK and c-Jun/AP-1 activation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.J Biomed Sci. 2006 Jan;13(1):143-56. doi: 10.1007/s11373-005-9037-7. Epub 2005 Nov 22. J Biomed Sci. 2006. PMID: 16328781
-
Caveolin-1 expression is critical for vascular endothelial growth factor-induced ischemic hindlimb collateralization and nitric oxide-mediated angiogenesis.Circ Res. 2004 Jul 23;95(2):154-61. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000136344.27825.72. Epub 2004 Jun 17. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15205364
-
Inhibition of activator protein 1 activation, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 in colon carcinoma cells: evidence for a redox-sensitive peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-independent mechanism.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5162-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0849. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289320
-
Endothelial caveolin-1 regulates pathologic angiogenesis in a mouse model of colitis.Gastroenterology. 2009 Feb;136(2):575-84.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.085. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19111727 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain residue phenylalanine 92 modulates Akt signaling.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 5;766:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.033. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26409042
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

