Phylogenetic estimates of SARS-CoV-2 introductions into Washington State
- PMID: 35013735
- PMCID: PMC8733893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100018
Phylogenetic estimates of SARS-CoV-2 introductions into Washington State
Abstract
Background: The first confirmed case of SARS-CoV-2 in North America was identified in Washington state on January 21, 2020. We aimed to quantify the number and temporal trends of out-of-state introductions of SARS-CoV-2 into Washington.
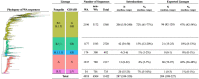
Methods: We conducted a molecular epidemiologic analysis of 11,422 publicly available whole genome SARS-CoV-2 sequences from GISAID sampled between December 2019 and September 2020. We used maximum parsimony ancestral state reconstruction methods on time-calibrated phylogenies to enumerate introductions/exports, their likely geographic source (US, non-US, and between eastern and western Washington), and estimated date of introduction. To incorporate phylogenetic uncertainty into our estimates, we conducted 5,000 replicate analyses by generating 25 random time-stratified samples of non-Washington reference sequences, 20 random polytomy resolutions, and 10 random resolutions of the reconstructed ancestral state.
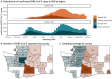
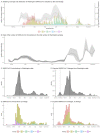
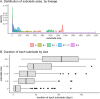
Findings: We estimated a minimum 287 introductions (range 244-320) into Washington and 204 exported lineages (range 188-227) of SARS-CoV-2 out of Washington. Introductions began in mid-January and peaked on March 29, 2020. Lineages with the Spike D614G variant accounted for the majority (88%) of introductions. Overall, 61% (range 55-65%) of introductions into Washington likely originated from a source elsewhere within the US, while the remaining 39% (range 35-45%) likely originated from outside of the US. Intra-state transmission accounted for 65% and 28% of introductions into eastern and western Washington, respectively.
Interpretation: The SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in Washington was continually seeded by a large number of introductions. Our findings highlight the importance of genomic surveillance to monitor for emerging variants due to high levels of inter- and intra-state transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
Funding source: None.
Keywords: Genomic analysis; Molecular epidemiology; Phylogeography; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
ALG reports personal fees from Abbott Molecular, grants from Merck, grants from Gilead, outside the submitted work. DMT, PR, LS, HX, KRJ, NB, MLH, MF and JTH have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Update of
-
Phylogenetic estimates of SARS-CoV-2 introductions into Washington State.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Apr 7:2021.04.05.21254924. doi: 10.1101/2021.04.05.21254924. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Lancet Reg Health Am. 2021 Sep;1:100018. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100018. PMID: 33855313 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Feb 12, 2021. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/(accessed.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

